Economic impact of dengue illness in the Americas
- PMID: 21292885
- PMCID: PMC3029168
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.10-0503
Economic impact of dengue illness in the Americas
Abstract
The growing burden of dengue in endemic countries and outbreaks in previously unaffected countries stress the need to assess the economic impact of this disease. This paper synthesizes existing studies to calculate the economic burden of dengue illness in the Americas from a societal perspective. Major data sources include national case reporting data from 2000 to 2007, prospective cost of illness studies, and analyses quantifying underreporting in national routine surveillance systems. Dengue illness in the Americas was estimated to cost $2.1 billion per year on average (in 2010 US dollars), with a range of $1-4 billion in sensitivity analyses and substantial year to year variation. The results highlight the substantial economic burden from dengue in the Americas. The burden for dengue exceeds that from other viral illnesses, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) or rotavirus. Because this study does not include some components (e.g., vector control), it may still underestimate total economic consequences of dengue.
Figures


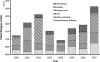
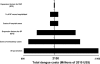
References
-
- Ooi EE, Gubler DJ. Global spread of epidemic dengue: the influence of environmental change. Future Virol. 2009;4:571–580.
-
- Halstead SB. Dengue. Lancet. 2007;370:1644–1652. - PubMed
-
- Suaya JA, Shepard DS, Siqueira JB, Martelli CT, Lum LC, Tan LH, Kongsin S, Jiamton S, Garrido F, Montoya R, Armien B, Huy R, Castillo L, Caram M, Sah BK, Sughayyar R, Tyo KR, Halstead SB. Cost of dengue cases in eight countries in the Americas and Asia: a prospective study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;80:846–855. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2002. http://www.who.int/docstore/wer/pdf/2002/wer7736.pdf Available at. Accessed September 7, 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

