The testis-enriched histone demethylase, KDM4D, regulates methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 during spermatogenesis in the mouse but is dispensable for fertility
- PMID: 21293030
- PMCID: PMC3099586
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.088955
The testis-enriched histone demethylase, KDM4D, regulates methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 during spermatogenesis in the mouse but is dispensable for fertility
Abstract
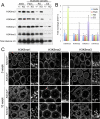
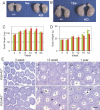
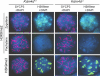
Epigenetic modifications, and methylation of histones in particular, dynamically change during spermatogenesis. Among various methylations of histone H3, methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) and its regulation are essential for spermatogenesis. Trimethytransferases as well as dimethyltransferase are required for meiotic progression. In addition, didemethylase of H3K9 is also critical for spermatogenesis through transcriptional regulation of spermatid-specific genes. However, the requirement for demethylation of trimethylated H3K9 (H3K9me3) during spermatogenesis remains to be elucidated. Here, we report the targeted disruption of KDM4D, a testis-enriched tridemethylase of H3K9. Kdm4d-null mice are viable and fertile and do not show any obvious phenotype. However, H3K9me3 accumulates significantly in Kdm4d-null round spermatids, and the distribution of methylated H3K9 in germ cells is dramatically changed. Nevertheless, the progression of spermatogenesis and the number of spermatozoa are normal, likely secondary to the earlier nuclear localization of another H3K9 tridemethylase, KDM4B, in Kdm4d-null elongating spermatids. These results suggest that demethylation of H3K9me3 in round spermatids is dispensable for spermatogenesis but that possible defects in Kdm4d-null elongating spermatids could be rescued by functional redundancy of the KDM4B demethylase.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Kdm4d mutant mice show impaired sperm motility and subfertility.J Reprod Dev. 2024 Oct 1;70(5):320-326. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2024-039. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Reprod Dev. 2024. PMID: 39034148 Free PMC article.
-
Jmjd1a demethylase-regulated histone modification is essential for cAMP-response element modulator-regulated gene expression and spermatogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2758-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066845. Epub 2009 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19910458 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-dependent chromatin localization of KDM4D lysine demethylase promotes H3K9me3 demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13026-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1021. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25378304 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone H3 lysine demethylases in glioblastoma.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Jun;42(2):445-454. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10114-1. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37286866 Review.
-
Epigenetic gene regulation by plant Jumonji group of histone demethylase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1809(8):421-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419882 Review.
Cited by
-
KDM4 Involvement in Breast Cancer and Possible Therapeutic Approaches.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 28;11:750315. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.750315. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34778065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Post-Translational Modifications and CircRNAs in Mouse and Human Spermatozoa: Potential Epigenetic Marks to Assess Human Sperm Quality.J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 27;9(3):640. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030640. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32121034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila Kdm4 demethylases in histone H3 lysine 9 demethylation and ecdysteroid signaling.Sci Rep. 2013 Oct 8;3:2894. doi: 10.1038/srep02894. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 24100631 Free PMC article.
-
KDM4/JMJD2 histone demethylases: epigenetic regulators in cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2013 May 15;73(10):2936-42. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4300. Epub 2013 May 3. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23644528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kdm4d mutant mice show impaired sperm motility and subfertility.J Reprod Dev. 2024 Oct 1;70(5):320-326. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2024-039. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Reprod Dev. 2024. PMID: 39034148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y. Histone lysine demethylases: emerging roles in development, physiology and disease. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 829 833 - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007; 128: 693 705 - PubMed
-
- Mosammaparast N, Shi Y. Reversal of histone methylation: biochemical and molecular mechanisms of histone demethylases. Annu Rev Biochem 2010; 79: 155 179 - PubMed
-
- Martin C, Zhang Y. The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 838 849 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

