MMSET regulates histone H4K20 methylation and 53BP1 accumulation at DNA damage sites
- PMID: 21293379
- PMCID: PMC3064261
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09658
MMSET regulates histone H4K20 methylation and 53BP1 accumulation at DNA damage sites
Abstract
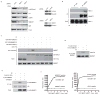
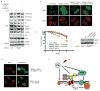
p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) is known to be an important mediator of the DNA damage response, with dimethylation of histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me2) critical to the recruitment of 53BP1 to double-strand breaks (DSBs). However, it is not clear how 53BP1 is specifically targeted to the sites of DNA damage, as the overall level of H4K20me2 does not seem to increase following DNA damage. It has been proposed that DNA breaks may cause exposure of methylated H4K20 previously buried within the chromosome; however, experimental evidence for such a model is lacking. Here we found that H4K20 methylation actually increases locally upon the induction of DSBs and that methylation of H4K20 at DSBs is mediated by the histone methyltransferase MMSET (also known as NSD2 or WHSC1) in mammals. Downregulation of MMSET significantly decreases H4K20 methylation at DSBs and the subsequent accumulation of 53BP1. Furthermore, we found that the recruitment of MMSET to DSBs requires the γH2AX-MDC1 pathway; specifically, the interaction between the MDC1 BRCT domain and phosphorylated Ser 102 of MMSET. Thus, we propose that a pathway involving γH2AX-MDC1-MMSET regulates the induction of H4K20 methylation on histones around DSBs, which, in turn, facilitates 53BP1 recruitment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Histone H4 deacetylation facilitates 53BP1 DNA damage signaling and double-strand break repair.J Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;5(3):157-65. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjs066. Epub 2013 Jan 16. J Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23329852
-
Impact of histone H4 lysine 20 methylation on 53BP1 responses to chromosomal double strand breaks.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049211. Epub 2012 Nov 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209566 Free PMC article.
-
53BP1-dependent robust localized KAP-1 phosphorylation is essential for heterochromatic DNA double-strand break repair.Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;12(2):177-84. doi: 10.1038/ncb2017. Epub 2010 Jan 17. Nat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20081839
-
The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21036673 Review.
-
Non-homologous end joining in class switch recombination: the beginning of the end.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Mar 12;364(1517):653-65. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0196. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19008195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Methyltransferase NSD2 as a Potential Oncogene in Human Solid Tumors.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 13;13:6837-6846. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S259873. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of multiple myeloma.Int J Clin Oncol. 2015 Jun;20(3):413-22. doi: 10.1007/s10147-015-0837-0. Epub 2015 May 8. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25953678 Review.
-
WHSC1 links transcription elongation to HIRA-mediated histone H3.3 deposition.EMBO J. 2013 Aug 28;32(17):2392-406. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.176. Epub 2013 Aug 6. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23921552 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-catalyzed H4K16me1 promotes 53BP1 recruitment to permit DNA damage repair and cell survival.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 2;47(21):10977-10993. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz897. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31612207 Free PMC article.
-
USP29 Deubiquitinates SETD8 and Regulates DNA Damage-Induced H4K20 Monomethylation and 53BP1 Focus Formation.Cells. 2022 Aug 11;11(16):2492. doi: 10.3390/cells11162492. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FitzGerald JE, Grenon M, Lowndes NF. 53BP1: function and mechanisms of focal recruitment. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37:897–904. - PubMed
-
- Sanders SL, et al. Methylation of histone H4 lysine 20 controls recruitment of Crb2 to sites of DNA damage. Cell. 2004;119:603–614. - PubMed
-
- Celeste A, et al. Histone H2AX phosphorylation is dispensable for the initial recognition of DNA breaks. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:675–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

