High glucose stimulates TNFα and MCP-1 expression in rat microglia via ROS and NF-κB pathways
- PMID: 21293471
- PMCID: PMC4009937
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.174
High glucose stimulates TNFα and MCP-1 expression in rat microglia via ROS and NF-κB pathways
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether high glucose stimulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines and the possible mechanisms involved.
Methods: ELISA and real-time PCR were used to determine the expression of the inflammatory factors, and a chemiluminescence assay was used to measure the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
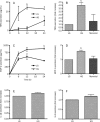
Results: Compared to low glucose (10 mmol/L), treatment with high glucose (35 mmol/L) increased the secretion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), but not interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, in a time-dependent manner in primary cultured rat microglia. The mRNA expression of TNFα and MCP-1 also increased in response to high glucose. This upregulation was specific to high glucose because it was not observed in the osmotic control. High-glucose treatment stimulated the formation of ROS. Furthermore, treatment with the ROS scavenger NAC significantly reduced the high glucose-induced TNFα and MCP-1 secretion. In addition, the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitors MG132 and PDTC completely blocked the high glucose-induced TNFα and MCP-1 secretion.
Conclusion: We found that high glucose induces TNFα and MCP-1 secretion as well as mRNA expression in rat microglia in vitro, and this effect is mediated by the ROS and NF-κB pathways.
Figures



References
-
- Gregersen R, Lambertsen K, Finsen B. Microglia and macrophages are the major source of tumor necrosis factor in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:53–65. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Wang T, Pei Z, Miller DS, Wu X, Block ML, et al. Aggregated alpha-synuclein activates microglia: a process leading to disease progression in Parkinson's disease. Faseb J. 2005;19:533–42. - PubMed
-
- Akama KT, Van Eldik LJ. Beta-amyloid stimulation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in astrocytes is interleukin-1beta- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha)-dependent, and involves a TNFalpha receptor-associated factor- and NFkappaB-inducing kinase-dependent signaling mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:7918–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

