N-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide promotes vascular endothelial cell angiogenesis and migration in the absence of serum and FGF-2
- PMID: 21293473
- PMCID: PMC4009934
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.201
N-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide promotes vascular endothelial cell angiogenesis and migration in the absence of serum and FGF-2
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of N-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide (BPC) on angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
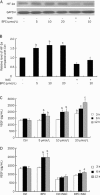
Methods: Capillary-like tube formation on matrigel and cell migration analyses were performed in the absence of serum and fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured using a fluorescent probe, 2', 7'- dichlorodihydrofluorescein (DCHF). The nitric oxide (NO) production of HUVECs was examined using a NO detection kit. Morphological observation under a phase contrast microscope, a viability assay using 3-[4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2, 5-diphenyl-tetrazolium (MTT) and a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity analysis by a detection kit were performed to evaluate the toxicity of BPC on HUVECs in the presence of serum and FGF-2. The level of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were measured by Western blot and ELISA, respectively.
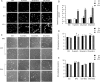
Results: In the absence of serum and FGF-2, cells treated with BPC (5-20 μmol/L) rapidly aligned with one another and formed tube-like structures within 12 h. In the presence of serum and FGF-2, cells treated with BPC for 24, 48 and 72 h had no changes in morphology, viability or LDH release compared with the control group. Cell migration in the BPC-treated group was significantly increased compared with the control group. During this process, NO production and ROS level were elevated dramatically, and the levels of HIF-1α and VEGF were increased dependent on the generation of ROS.
Conclusion: BPC most effectively promoted angiogenesis and migration in HUVECs in the absence of FGF-2 and serum.
Figures




References
-
- Chunga BH, Leec JJ, Kimb JD, Jeoungd D, Leed H, Choe J, et al. Angiogenic activity of sesamin through the activation of multiple signal pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;391:254–60. - PubMed
-
- Xia Y, Fan CD, Zhao BX, Zhao J, Shin DS, Miao JY. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel 1-arylmethyl-3-aryl-1H-pyrazole-5-carbohydrazide hydrazone derivatives as potential agents against A549 lung cancer cells. Eur J Med Chem. 2008;43:2347–53. - PubMed
-
- Fan CD, Zhao BX, Wei F, Zhang GH, Dong WL, Miao JY. Synthesis and discovery of autophagy inducers for A549 and H460 lung cancer cells, novel 1-(2′-hydroxy-3′-aroxypropyl)-3-aryl-1H-pyrazole-5-carbohydrazide derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18:3860–4. - PubMed
-
- Zhao BX, Zhang L, Zhu XS, Wan MS, Zhao J, Zhang Y, et al. Synthesis and discovery of a novel pyrazole derivative as an inhibitor of apoptosis through modulating integrin beta4, ROS, and p53 levels in vascular endothelial cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16:5171–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

