NF-κB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 21293511
- PMCID: PMC3295539
- DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.213
NF-κB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
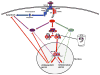
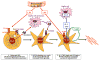
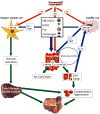
Hepatic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are the most common causes of death in patients with chronic liver disease. Chronic liver injury of virtually any etiology triggers inflammatory and wound-healing responses that in the long run promote the development of hepatic fibrosis and HCC. Here, we review the role of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), a master regulator of inflammation and cell death, in the development of hepatocellular injury, liver fibrosis and HCC, with a particular focus on the role of NF-κB in different cellular compartments of the liver. We propose that NF-κB acts as a central link between hepatic injury, fibrosis and HCC, and that it may represent a target for the prevention or treatment of liver fibrosis and HCC. However, NF-κB acts as a two-edged sword and inhibition of NF-κB may not only exert beneficial effects but also negatively impact hepatocyte viability, especially when NF-κB inhibition is pronounced. Finding appropriate targets or identifying drugs that either exert only a moderate effect on NF-κB activity or that can be specifically delivered to nonparenchymal cells will be essential to avoid the increase in liver injury associated with complete NF-κB blockade in hepatocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S35–50. - PubMed
-
- Bonacchi A, et al. The chemokine CCL21 modulates lymphocyte recruitment and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1060–76. - PubMed
-
- Seki E, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007;13:1324–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

