Phenotypic variability in a French family with a novel mutation in the BEST1 gene causing multifocal best vitelliform macular dystrophy
- PMID: 21293734
- PMCID: PMC3032275
Phenotypic variability in a French family with a novel mutation in the BEST1 gene causing multifocal best vitelliform macular dystrophy
Abstract
Aims: To describe genetic and clinical findings in a French family affected by best vitelliform macular dystrophy (BVMD).
Methods: We screened eight at-risk members of a family, including a BVMD-affected proband, by direct sequencing of 11 bestrophin-1 (BEST1) exons. Individuals underwent ophthalmic examination and autofluorescent fundus imaging, indocyanine green angiography, electro-oculogram (EOG), electroretinogram (ERG), multifocal ERG, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and where possible, spectral domain OCT.
Results: The sequence analysis of the BEST1 gene revealed one previously unknown mutation, c.15C>A (p.Y5X), in two family members and one recently described mutation, c.430A>G (p.S144G), in five family members. Fundus examination and electrophysiological responses provided no evidence of the disease in the patient carrying only the p.Y5X mutation. Three patients with the p.S144G mutation did not show any preclinical sign of BVMD except altered EOGs. Two individuals of the family exhibited a particularly severe phenotype of multifocal BVMD-one individual carrying the p.S144G mutation heterozygously and one individual harboring both BEST1 mutations (p.S144G inherited from his mother and p.Y5X from his father). Both of these family members had multifocal vitelliform autofluorescent lesions combined with abnormal EOG, and the spectral domain OCT displayed a serous retinal detachment. In addition, ERGs demonstrated widespread retinal degeneration and multifocal ERGs showed a reduction in the central retina function, which could be correlated with the decreased visual acuity and visual field scotomas.
Conclusions: A thorough clinical evaluation found no pathological phenotype in the patient carrying the isolated p.Y5X mutation. The patients carrying the p.S144G variation in the protein exhibited considerable intrafamilial phenotypic variability. Two young affected patients in this family exhibited an early onset, severe, multifocal BVMD with a diffuse distribution of autofluorescent deposits throughout the retina and rapid evolution toward the loss of central vision. The other genetically affected relatives had only abnormal EOGs and displayed no or extremely slow electrophysiological evolution.
Figures




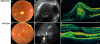

References
-
- Petrukhin K, Koisti MJ, Bakall B, Li W, Xie G, Marknell T, Sandgren O, Forsman K, Holmgren G, Andreasson S, Vujic M, Bergen AA, McGarty-Dugan V, Figueroa D, Austin CP, Metzker ML, Caskey CT, Wadelius C. Identification of the gene responsible for Best macular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1998;19:241–7. - PubMed
-
- Marquardt A, Stohr H, Passmore LA, Kramer F, Rivera A, Weber BH. Mutations in a novel gene, VMD2, encoding a protein of unknown properties cause juvenile-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy (Best's disease). Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1517–25. - PubMed
-
- Krämer F, White K, Pauleikhoff D, Gehrig A, Passmore L, Rivera A, Rudolph G, Kellner U, Andrassi M, Lorenz B, Rohrschneider K, Blankenagel A, Jurklies B, Schilling H, Schütt F, Holz FG, Weber BH. Mutations in the VMD2 gene are associated with juvenile-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy (Best disease) and adult vitelliform macular dystrophy but not age-related macular degeneration. Eur J Hum Genet. 2000;8:286–92. - PubMed
-
- Lotery AJ, Munier FL, Fishman GA, Weleber RG, Jacobson SG, Affatigato LM, Nichols BE, Schorderet DF, Sheffield VC, Stone EM. Allelic variation in the VMD2 gene in best disease and age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:1291–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
