A memory-based model of Hick's law
- PMID: 21293788
- PMCID: PMC3031137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cogpsych.2010.11.001
A memory-based model of Hick's law
Abstract
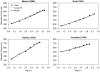
We propose and evaluate a memory-based model of Hick's law, the approximately linear increase in choice reaction time with the logarithm of set size (the number of stimulus-response alternatives). According to the model, Hick's law reflects a combination of associative interference during retrieval from declarative memory and occasional savings for stimulus-response repetitions due to non-retrieval. Fits to existing data sets show that the model accounts for the basic set-size effect, changes in the set-size effect with practice, and stimulus-response repetition effects that challenge the information-theoretic view of Hick's law. We derive the model's prediction of an interaction between set size, stimulus fan (the number of responses associated with a particular stimulus), and stimulus-response transition, which is subsequently tested and confirmed in two experiments. Collectively, the results support the core structure of the model and its explanation of Hick's law in terms of basic memory effects.
Keywords: Hick’s law; choice reaction time; cognitive modeling; fan effect; memory.
Figures







References
-
- Anderson JR. Retrieval of propositional information from long-term memory. Cognitive Psychology. 1974;6:451–474.
-
- Anderson JR. Language, memory, and thought. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1976.
-
- Anderson JR. Interference: The relationship between response latency and response accuracy. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory. 1981;7:326–343.
-
- Anderson JR. How can the human mind occur in the physical universe? New York: Oxford University Press; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

