Transferred NOESY NMR studies of biotin mimetic peptide (FSHPQNT) bound to streptavidin: a structural model for studies of peptide-protein interactions
- PMID: 21294848
- PMCID: PMC3115400
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01096.x
Transferred NOESY NMR studies of biotin mimetic peptide (FSHPQNT) bound to streptavidin: a structural model for studies of peptide-protein interactions
Abstract
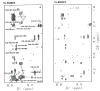
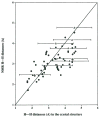
Protein-protein interactions control signaling, specific adhesion, and many other biological functions. The three-dimensional structures of the interfaces and bound ligand can be approached with transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy NMR, which can be applied to much larger proteins than conventional NMR and requires less concentrated protein. However, it is not clear how accurately the structures of protein-bound peptides can be determined by transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy. We studied the structure of a biotin mimetic peptide (FSHPQNT) bound to streptavidin, because the X-ray structure of the complex is available to 1.74 Å resolution, and we found that conditions could be adjusted so that the off-rates were fast enough for transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy NMR. The off-rate was determined with (19)F NMR, using a para-fluoro-phenylalanine analog of the peptide. A new criterion for a lower limit on kinetic off-rate was found, which allowed accurate structure determination at a slower off-rate. Non-specific binding of the peptide to streptavidin was not significant, because biotin blocked the peptide transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy. Protein mediation for the long-range peptide transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy cross-peaks was corrected by a transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy/ROESY averaging procedure. The protein-bound structure of the peptide was determined by transferred nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy constrained and simulated annealing. The structure deduced from the NMR was close to the X-ray structure.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures








References
-
- Jones S, Thornton JM. Analysis of protein-protein interaction sites using surface patches. J Mol Biol. 1997;272:121–32. - PubMed
-
- Gizachew D, Moffett DB, Busse SC, Westler WM, Dratz EA, Teintze M. NMR studies on the conformation of the CD4 36–59 peptide bound to HIV-1 gp120. Biochemistry. 1998;37:10616–25. - PubMed
-
- Cortese R, Monaci P, Luzzago A, Santini C, Bartoli F, Cortese I, et al. Selection of biologically active peptides by phage display of random peptide libraries. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1996;7:616–21. - PubMed
-
- Rarick HM, Artemyev NO, Mills JS, Skiba NP, Hamm HE. Specific peptide probes for G-protein interaction with effectors. Methods Enzymol. 1994;238:13–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

