Applying molecular dynamics simulations to identify rarely sampled ligand-bound conformational states of undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase, an antibacterial target
- PMID: 21294851
- PMCID: PMC3095679
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01101.x
Applying molecular dynamics simulations to identify rarely sampled ligand-bound conformational states of undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase, an antibacterial target
Abstract
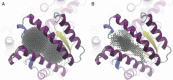
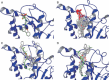
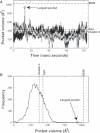
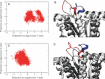
Undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase is a cis-prenyltransferase enzyme, which is required for cell wall biosynthesis in bacteria. Undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase is an attractive target for antimicrobial therapy. We performed long molecular dynamics simulations and docking studies on undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase to investigate its dynamic behavior and the influence of protein flexibility on the design of undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase inhibitors. We also describe the first X-ray crystallographic structure of Escherichia coli apo-undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase. The molecular dynamics simulations indicate that undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase is a highly flexible protein, with mobile binding pockets in the active site. By carrying out docking studies with experimentally validated undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase inhibitors using high- and low-populated conformational states extracted from the molecular dynamics simulations, we show that structurally dissimilar compounds can bind preferentially to different and rarely sampled conformational states. By performing structural analyses on the newly obtained apo-undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase and other crystal structures previously published, we show that the changes observed during the molecular dynamics simulation are very similar to those seen in the crystal structures obtained in the presence or absence of ligands. We believe that this is the first time that a rare 'expanded pocket' state, key to drug design and verified by crystallography, has been extracted from a molecular dynamics simulation.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures


References
-
- Rohdich F, Bacher A, Eisenreich W. Isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways as anti-infective drug targets. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33:785–791. - PubMed
-
- Ko TP, Chen YK, Robinson H, Tsai PC, Gao YG, Chen AP, Wang AH, Liang PH. Mechanism of product chain length determination and the role of a flexible loop in Escherichia coli undecaprenyl-pyrophosphate synthase catalysis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:47474–47482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

