The use of some nanoemulsions based on aqueous propolis and lycopene extract in the skin's protective mechanisms against UVA radiation
- PMID: 21294875
- PMCID: PMC3042917
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-3
The use of some nanoemulsions based on aqueous propolis and lycopene extract in the skin's protective mechanisms against UVA radiation
Abstract
Background: The use of natural products based on aqueous extract of propolis and lycopene in the skin's protective mechanisms against UVA radiation was evaluated by means of experimental acute inflammation on rat paw edema. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the harmlessness of propolis - lycopene system through evaluation of skin level changes and anti-inflammatory action. The regenerative and protective effect of the aqueous propolis and lycopene extract is based on its richness in biologically active substances such as: tocopherols, flavonoids, amino acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, the chlorophyll pigment, all substances with strong antioxidant activity, that modify the oxidative stress, mainly by reducing the prooxidant processes and enhancing the antioxidant ones. These substances participate in the synthesis of prostaglandins and phospholipids components of cell membrane thus enhancing skin protection mechanisms.
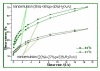
Results: The experimental systems offered a sustained release of the drug, in vitro, for aim eight hours. The prepared formulations aim did not reveal a deteriorating effect on tissues. They proved a better therapeutic efficiency Compared to standard suspension, they provided a better therapeutic efficiency coupled with extended time interval of tested parameters (24 hours). Preliminary examination of tissues showed that the experimental formulations did not irritate. Local application of propolis and lycopene aqueous extract nanoemulsion has a high potential both regarding its efficiency (the analgesic effect) and therapeutic safety.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that propolis and lycopene extract nanoemulsions, preparations contains active substances, can confer better therapeutic effects than those of the conventional formulations, based on local control-release of dozed form, for a longer period of time, which probably improve its efficiency and skin acceptance, meaning a better compliance. The information obtained in the present study suggests that administration of propolis and lycopene aqueous extract nanoemulsion is safe. The preparation can be useful for further preclinical studies lycopene embedded in aqueous propolis extract to be used in pharmaceuticals (targeted medical therapy).
Figures




References
-
- Applegate LA, Frenk E. Cellular defense mechanisms of the skin against oxidant stress and in particular UVA radiation. Eur.J.Dermatol. 1995;5:97–103. doi: 10.1016/0926-9959(95)90037-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

