Inhibition of RhoA GTPase and the subsequent activation of PTP1B protects cultured hippocampal neurons against amyloid β toxicity
- PMID: 21294893
- PMCID: PMC3038970
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-14
Inhibition of RhoA GTPase and the subsequent activation of PTP1B protects cultured hippocampal neurons against amyloid β toxicity
Abstract
Background: Amyloid beta (Aβ) is the main agent responsible for the advent and progression of Alzheimer's disease. This peptide can at least partially antagonize nerve growth factor (NGF) signalling in neurons, which may be responsible for some of the effects produced by Aβ. Accordingly, better understanding the NGF signalling pathway may provide clues as to how to protect neurons from the toxic effects of Aβ.
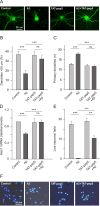
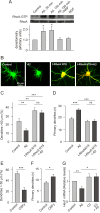
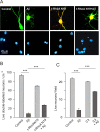
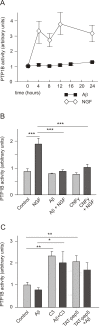
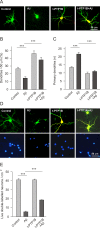
Results: We show here that Aβ activates the RhoA GTPase by binding to p75NTR, thereby preventing the NGF-induced activation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) that is required for neuron survival. We also show that the inactivation of RhoA GTPase and the activation of PTP1B protect cultured hippocampal neurons against the noxious effects of Aβ. Indeed, either pharmacological inhibition of RhoA with C3 ADP ribosyl transferase or the transfection of cultured neurons with a dominant negative form of RhoA protects cultured hippocampal neurons from the effects of Aβ. In addition, over-expression of PTP1B also prevents the deleterious effects of Aβ on cultured hippocampal neurons.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that potentiating the activity of NGF at the level of RhoA inactivation and PTP1B activation may represent a new means to combat the noxious effects of Aβ in Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
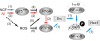
Similar articles
-
Neuronal Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Hastens Amyloid β-Associated Alzheimer's Disease in Mice.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 12;40(7):1581-1593. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2120-19.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 8. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31915254 Free PMC article.
-
NGF-activated protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B mediates the phosphorylation and degradation of I-kappa-Balpha coupled to NF-kappa-B activation, thereby controlling dendrite morphology.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010 Apr;43(4):384-93. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20123020
-
Production of nerve growth factor by beta-amyloid-stimulated astrocytes induces p75NTR-dependent tau hyperphosphorylation in cultured hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Oct;84(5):1098-106. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20996. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16862561
-
Amyloid beta serves as an NGF-like neurotrophic factor or acts as a NGF antagonist depending on its concentration.J Neurochem. 2009 Dec;111(6):1425-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06412.x. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 20050289
-
NGF and the Amyloid Precursor Protein in Alzheimer's Disease: From Molecular Players to Neuronal Circuits.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1331:145-165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-74046-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34453297 Review.
Cited by
-
The protection of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor on β-amyloid-induced the injury of neurite outgrowth via regulating axon guidance related genes expression in neuronal cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):900-13. Epub 2012 Oct 20. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23119107 Free PMC article.
-
Deconstructing signal transduction pathways that regulate the actin cytoskeleton in dendritic spines.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012 Jul;69(7):426-41. doi: 10.1002/cm.21015. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22307832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights on the regulators and inhibitors of RhoA-ROCK signalling in Parkinson's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jan 7;40(1):90. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01500-x. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39775342 Review.
-
Rho Signaling in Synaptic Plasticity, Memory, and Brain Disorders.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 4;9:729076. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.729076. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34671600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease Induced by Amyloid-β and Tau Phosphorylation Along with RhoA Activity: Perspective of RhoA/Rho-Associated Protein Kinase Inhibitors for Neuronal Therapy.Cells. 2025 Jan 10;14(2):89. doi: 10.3390/cells14020089. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

