Respective implications of glutamate decarboxylase antibodies in stiff person syndrome and cerebellar ataxia
- PMID: 21294897
- PMCID: PMC3042903
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-6-3
Respective implications of glutamate decarboxylase antibodies in stiff person syndrome and cerebellar ataxia
Abstract
Background: To investigate whether Stiff-person syndrome (SPS) and cerebellar ataxia (CA) are associated with distinct GAD65-Ab epitope specificities and neuronal effects.
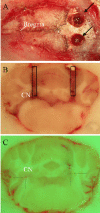
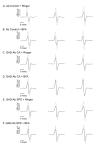
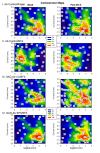
Methods: Purified GAD65-Ab from neurological patients and monoclonal GAD65-Ab with distinct epitope specificities (b78 and b96.11) were administered in vivo to rat cerebellum. Effects of intra-cerebellar administration of GAD65-Ab were determined using neurophysiological and neurochemical methods.
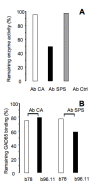
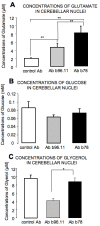
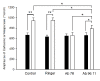
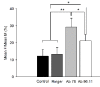
Results: Intra-cerebellar administration of GAD65-Ab from a SPS patient (Ab SPS) impaired the NMDA-mediated turnover of glutamate, but had no effect on NMDA-mediated turnover of glycerol. By contrast, GAD65-Ab from a patient with cerebellar ataxia (Ab CA) markedly decreased the NMDA-mediated turnover of glycerol. Both GAD65-Ab increased the excitability of the spinal cord, as assessed by the F wave/M wave ratios. The administration of BFA, an inhibitor of the recycling of vesicles, followed by high-frequency stimulation of the cerebellum, severely impaired the cerebello-cortical inhibition only when Ab CA was used. Moreover, administration of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) of the motor cortex revealed a strong disinhibition of the motor cortex with Ab CA. Monoclonal antibodies b78 and b96.11 showed distinct effects, with greater effects of b78 in terms of increase of glutamate concentrations, impairment of the adaptation of the motor cortex to repetitive peripheral stimulation, disinhibition of the motor cortex following tDCS, and increase of the F/M ratios. Ab SPS shared antibody characteristics with b78, both in epitope recognition and ability to inhibit enzyme activity, while Ab CA had no effect on GAD65 enzyme activity.
Conclusions: These results suggest that, in vivo, neurological impairments caused by GAD65-Ab could vary according to epitope specificities. These results could explain the different neurological syndromes observed in patients with GAD65-Ab.
Figures

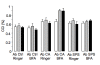


References
-
- Honnorat J, Saiz A, Giometto B, Vincent A, Brieva L, de Andres C, Maestre J, Fabien N, Vighetto A, Casamitjana R, Thivolet C, Tavolato B, Antoine J, Trouillas P, Graus F. Cerebellar ataxia with anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: study of 14 patients. Arch Neurol. 2001;58(2):225–30. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.2.225. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot HJ, Christgau S, Reetz A, Solimena M, Cascalho M, Folli F, Richter-Olesen H, De Camilli P. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990;347(6289):151–6. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

