Plasma peptidome profiling of acute hepatitis E patients by MALDI-TOF/TOF
- PMID: 21294899
- PMCID: PMC3042370
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-9-5
Plasma peptidome profiling of acute hepatitis E patients by MALDI-TOF/TOF
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis E is endemic to resource-poor regions, where it manifests as sporadic cases and large waterborne outbreaks. The disease severity ranges from acute self-limited hepatitis with low mortality to fulminant hepatic failure with high mortality. It is believed that the host response plays an important role in determining the progression and outcome of this disease. We profiled the plasma peptidome from hepatitis E patients to discover suitable biomarkers and understand disease pathogenesis.
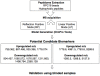
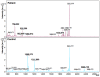
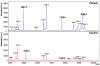
Results: The peptidome (< 10 kDa) fraction of plasma was enriched and analyzed by mass spectrometry. A comparative analysis of the peptide pattern of hepatitis E patients versus healthy controls was performed using ClinPro Tools. We generated a peptide profile that could be used for selective identification of hepatitis E cases. We have identified five potential biomarker peaks with m/z values of 9288.6, 7763.6, 4961.5, 1060.572 and 2365.139 that can be used to reliably differentiate between hepatitis E patients and controls with areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) values of 1.00, 0.954, 0.989, 0.960 and 0.829 respectively. A number of proteins involved in innate immunity were identified to be differentially present in the plasma of patients compared to healthy controls.
Conclusions: Besides the utility of this approach for biomarker discovery, identification of changes in endogenous peptides in hepatitis E patient plasma has increased our understanding of disease pathogenesis. We have identified peptides in plasma that can reliably distinguish hepatitis E patients from healthy controls. Results from this and an earlier proteomics study are discussed.
Figures






References
-
- Jameel S. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. Expert Rev Mol Med. 1999;1999:1–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

