Time controlled release of arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C) from agarose hydrogels using layer-by-layer assembly: an in vitro study
- PMID: 21294967
- PMCID: PMC3873741
- DOI: 10.1163/092050610X552221
Time controlled release of arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C) from agarose hydrogels using layer-by-layer assembly: an in vitro study
Abstract
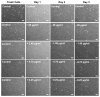
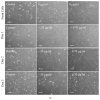
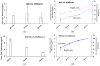
Experimentally induced axonal regeneration is compromised by glial scar formation arising from leptomeningeal fibroblasts cells in and around the hydrogel scaffold implanted for nerve repair. Strategies are needed to prevent such fibroblastic reactive cell layer formation for enhanced axonal regeneration. Here, we implement the technique of layer-by-layer assembled degradable, hydrogen bonded multilayers on agarose hydrogels to incorporate an anti-mitotic drug (1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C)) within the agarose hydrogels. We show controlled release of Ara-C under physiological conditions over a period of days. The concentrations of Ara-C released from agarose at the different time points were sufficient to inhibit fibroblast growth in vitro, while not adversely affecting the viability of the neuronal cells.
Figures













References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
