Effects of testosterone on spatial learning and memory in adult male rats
- PMID: 21295035
- PMCID: PMC3081396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.01.009
Effects of testosterone on spatial learning and memory in adult male rats
Abstract
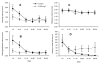
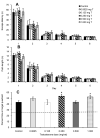
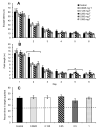
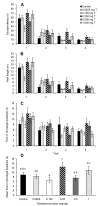
A male advantage over females for spatial tasks has been well documented in both humans and rodents, but it remains unclear how the activational effects of testosterone influence spatial ability in males. In a series of experiments, we tested how injections of testosterone influenced the spatial working and reference memory of castrated male rats. In the eight-arm radial maze, testosterone injections (0.500 mg/rat) reduced the number of working memory errors during the early blocks of testing but had no effect on the number of reference memory errors relative to the castrated control group. In a reference memory version of the Morris water maze, injections of a wide range of testosterone doses (0.0625-1.000 mg/rat) reduced path lengths to the hidden platform, indicative of improved spatial learning. This improved learning was independent of testosterone dose, with all treatment groups showing better performance than the castrated control males. Furthermore, this effect was only observed when rats were given testosterone injections starting 7 days prior to water maze testing and not when injections were given only on the testing days. We also observed that certain doses of testosterone (0.250 and 1.000 mg/rat) increased perseverative behavior in a reversal-learning task. Finally, testosterone did not have a clear effect on spatial working memory in the Morris water maze, although intermediate doses seemed to optimize performance. Overall, the results indicate that testosterone can have positive activational effects on spatial learning and memory, but the duration of testosterone replacement and the nature of the spatial task modify these effects.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Astur RS, Ortiz ML, Sutherland RJ. A characterization of performance by men and women in a virtual Morris water maze: A large and reliable sex difference. Behav. Brain Res. 1998;93:185–190. - PubMed
-
- Aultman JM, Moghaddam B. Distinct contributions of glutamate and dopamine receptors to temporal aspects of rodent working memory using a clinically relevant task. Psychopharmacology. 2001;153:353–364. - PubMed
-
- Bartke A, Steele RE, Musto N, Caldwell BV. Fluctuations in plasma testosterone levels in adult male rats and mice. Endocrinology. 1973;92:1223–1228. - PubMed
-
- Beer TM, Bland LB, Bussiere JR, Neiss MB, Wersinger EM, Garzotto M, Ryan CW, Janowsky JS. Testosterone loss and estradiol administration modify memory in men. J. Urol. 2006;175:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Beiko J, Lander R, Hampson E, Boon F, Cain DP. Contribution of sex differences in the acute stress response to sex differences in water maze performance. Behav. Brain Res. 2004;151:239–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

