Cognitive enhancers for facilitating drug cue extinction: insights from animal models
- PMID: 21295059
- PMCID: PMC3114302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.01.018
Cognitive enhancers for facilitating drug cue extinction: insights from animal models
Abstract
Given the success of cue exposure (extinction) therapy combined with a cognitive enhancer for reducing anxiety, it is anticipated that this approach will prove more efficacious than exposure therapy alone in preventing relapse in individuals with substance use disorders. Several factors may undermine the efficacy of exposure therapy for substance use disorders, but we suspect that neurocognitive impairments associated with chronic drug use are an important contributing factor. Numerous insights on these issues are gained from research using animal models of addiction. In this review, the relationship between brain sites whose learning, memory and executive functions are impaired by chronic drug use and brain sites that are important for effective drug cue extinction learning is explored first. This is followed by an overview of animal research showing improved treatment outcome for drug addiction (e.g. alcohol, amphetamine, cocaine, heroin) when explicit extinction training is conducted in combination with acute dosing of a cognitive-enhancing drug. The mechanism by which cognitive enhancers are thought to exert their benefits is by facilitating consolidation of drug cue extinction memory after activation of glutamatergic receptors. Based on the encouraging work in animals, factors that may be important for the treatment of drug addiction are considered.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Nic Dhonnchadha declares no conflicts of interest. Over the past 3 years, Dr. Kantak reports consulting fees and stock options from Yaupon Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures
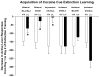
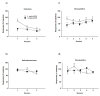
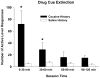
References
-
- Abe T, Sugihara H, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13361–13368. - PubMed
-
- Adair JC, Knoefel JE, Morgan N. Controlled trial of N-acetylcysteine for patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 2001;57:1515–1517. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JD, Pouzet B. Spatial memory deficits induced by perinatal treatment of rats with PCP and reversal effect of D-serine. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004;29:1080–1090. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JM, Fonnum F, Myhrer T. D-Serine alleviates retrograde amnesia of a visual discrimination task in rats with a lesion of the perirhinal cortex. Brain Res. 2003;979:240–244. - PubMed

