Whole-exome sequencing links a variant in DHDDS to retinitis pigmentosa
- PMID: 21295283
- PMCID: PMC3035708
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.01.001
Whole-exome sequencing links a variant in DHDDS to retinitis pigmentosa
Abstract
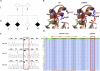
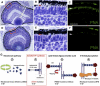
Increasingly, mutations in genes causing Mendelian disease will be supported by individual and small families only; however, exome sequencing studies have thus far focused on syndromic phenotypes characterized by low locus heterogeneity. In contrast, retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is caused by >50 known genes, which still explain only half of the clinical cases. In a single, one-generation, nonsyndromic RP family, we have identified a gene, dehydrodolichol diphosphate synthase (DHDDS), demonstrating the power of combining whole-exome sequencing with rapid in vivo studies. DHDDS is a highly conserved essential enzyme for dolichol synthesis, permitting global N-linked glycosylation. Zebrafish studies showed virtually identical photoreceptor defects as observed with N-linked glycosylation-interfering mutations in the light-sensing protein rhodopsin. The identified Lys42Glu variant likely arose from an ancestral founder, because eight of the nine identified alleles in 27,174 control chromosomes were of confirmed Ashkenazi Jewish ethnicity. These findings demonstrate the power of exome sequencing linked to functional studies when faced with challenging study designs and, importantly, link RP to the pathways of N-linked glycosylation, which promise new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
Copyright © 2011 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Heckenlively J.R., Yoser S.L., Friedman L.H., Oversier J.J. Clinical findings and common symptoms in retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1988;105:504–511. - PubMed
-
- Pagon R.A. Retinitis pigmentosa. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1988;33:137–177. - PubMed
-
- Hartong D.T., Berson E.L., Dryja T.P. Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet. 2006;368:1795–1809. - PubMed
-
- Price A.L., Patterson N.J., Plenge R.M., Weinblatt M.E., Shadick N.A., Reich D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:904–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

