Review: hCG, preeclampsia and regulatory T cells
- PMID: 21295851
- PMCID: PMC3061407
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.01.009
Review: hCG, preeclampsia and regulatory T cells
Abstract
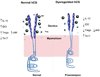
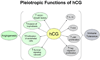
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is crucial for successful pregnancy. Its many functions include angiogenesis and immune regulation. Despite years of research, the etiology of preeclampsia remains unknown. Marked by insufficient trophoblast invasion and poor spiral artery remodeling, preeclampsia has also been linked to immune dysregulation. Here we discuss the roles of hCG in the context of endovascular cross-talk between trophoblasts and endothelial cells and immune tolerance. We propose that functional and glycosylation modifications of hCG may contribute to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Meekins JW, Pijnenborg R, Hanssens M, McFadyen IR, van Asshe A. A study of placental bed spiral arteries and trophoblast invasion in normal and severe pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994;101:669–674. - PubMed
-
- Toldi G, Svec P, Vasarhelyi B, Meszaros G, Rigo J, Tulassay T, Treszi A. Decreased number of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in preeclampsia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87:1229–1233. - PubMed
-
- Williams PJ, Bulmer JN, Searle RF, Innes BA, Robson SC. Altered decidual leucocyte populations in the placental bed in pre-eclampsia and foetal growth restriction: a comparison with late normal pregnancy. Reproduction. 2009;138:177–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

