Methodology and application of flow cytometry for investigation of human malaria parasites
- PMID: 21296083
- PMCID: PMC3071436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.01.015
Methodology and application of flow cytometry for investigation of human malaria parasites
Abstract
Historically, examinations of the inhibition of malaria parasite growth/invasion, whether using drugs or antibodies, have relied on the use of microscopy or radioactive hypoxanthine uptake. These are considered gold standards for measuring the effectiveness of antimalarial treatments, however, these methods have well known shortcomings. With the advent of flow cytometry coupled with the use of fluorescent DNA stains allowed for increased speed, reproducibility, and qualitative estimates of the effectiveness of antibodies and drugs to limit malaria parasite growth which addresses the challenges of traditional techniques. Because materials and machines available to research facilities are so varied, different methods have been developed to investigate malaria parasites by flow cytometry. This review is intended to serve as a reference guide for advanced users and importantly, as a primer for new users, to support expanded use and improvements to malaria flow cytometry, particularly in endemic countries.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
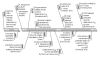

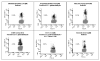
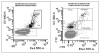
References
-
- Ahlborg N, Iqbal J, Bjork L, Stahl S, Perlmann P, Berzins K. Plasmodium falciparum: differential parasite growth inhibition mediated by antibodies to the antigens Pf332 and Pf155/RESA. Exp Parasitol. 1996;82:155–63. - PubMed
-
- Angulo-Barturen I, Jimenez-Diaz MB, Mulet T, Rullas J, Herreros E, Ferrer S, Jimenez E, Mendoza A, Regadera J, Rosenthal PJ, Bathurst I, Pompliano DL, de las Heras F. Gomez, Gargallo-Viola D. A murine model of falciparum-malaria by in vivo selection of competent strains in non-myelodepleted mice engrafted with human erythrocytes. PLoS One. 2008;3:e2252. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arndt-Jovin DJ, Jovin TM. Analysis and sorting of living cells according to deoxyribonucleic acid content. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977;25:585–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

