Cystatin C and albuminuria as risk factors for development of CKD stage 3: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
- PMID: 21296473
- PMCID: PMC3090544
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.11.021
Cystatin C and albuminuria as risk factors for development of CKD stage 3: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
Abstract
Background: The growing burden and morbidity of chronic kidney disease (CKD) warrant effective strategies for identifying those at increased risk. We examined the association of cystatin C level and albuminuria with the development of CKD stage 3.
Study design: Prospective observational study.
Setting & participants: 5,422 participants from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m(2).
Predictor: Participants were categorized into 4 mutually exclusive groups: the presence or absence of microalbuminuria (albumin-creatinine ratio >17 and >25 μg/mg in men and women, respectively) in those with or without cystatin C level ≥1.0 mg/L.
Outcomes & measurements: Incident CKD stage 3 was defined as eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m(2) at the third or fourth visit and an annual decrease >1 mL/min/1.73 m(2). Poisson regression was used to evaluate incident rate ratios in unadjusted and adjusted analyses that include baseline eGFR.
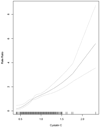
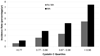
Results: Mean age was 61 years, 49% were men, 38% were white, 11% had diabetes, 13.7% had cystatin C level ≥1 mg/L, 8.4% had microalbuminuria, and 2.7% had cystatin C level ≥1 mg/L with microalbuminuria. 554 (10%) participants developed CKD stage 3 during a median follow-up of 4.7 years, and adjusted incidence rate ratios were 1.57 (95% CI, 1.19-2.07), 1.37 (95% CI, 1.13-1.66), and 2.12 (95% CI, 1.61-2.80) in those with microalbuminuria, cystatin C level ≥1 mg/L, and both, respectively, compared with those with neither.
Limitations: Relatively short follow-up and absence of measured GFR.
Conclusions: Cystatin C level and microalbuminuria are independent risk factors for incident CKD stage 3 and could be useful as screening tools to identify those at increased risk.
Copyright © 2011 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
N section :
Figures
Comment in
-
Predicting development of CKD in the general population--early days in a rapidly evolving field.Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Jun;57(6):805-7. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.02.378. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011. PMID: 21601124 No abstract available.
References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9(12) Suppl:S16–S23. - PubMed
-
- Fried LF, Shlipak MG, Crump C, et al. Renal insufficiency as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in elderly individuals. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(8):1364–1372. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Eng J Med. 2004;351(13):1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Manjunath G, Tighiouart H, Coresh J, et al. Level of kidney function as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in the elderly. Kidney Int. 2003;63(3):1121–1129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 078204/PHS HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025015/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK078204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

