CK2 phosphorylation of an acidic Ser/Thr di-isoleucine motif in the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE5 isoform promotes association with beta-arrestin2 and endocytosis
- PMID: 21296876
- PMCID: PMC3064201
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.182881
CK2 phosphorylation of an acidic Ser/Thr di-isoleucine motif in the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE5 isoform promotes association with beta-arrestin2 and endocytosis
Abstract
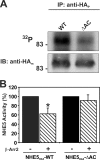
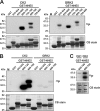
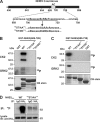
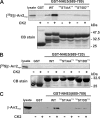
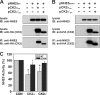
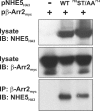
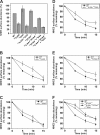
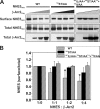
Internalization of the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE5 into recycling endosomes is enhanced by the endocytic adaptor proteins β-arrestin1 and -2, best known for their preferential recognition of ligand-activated G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). However, the mechanism underlying their atypical association with non-GPCRs, such as NHE5, is unknown. In this study, we identified a highly acidic, serine/threonine-rich, di-isoleucine motif (amino acids 697-723) in the cytoplasmic C terminus of NHE5 that is recognized by β-arrestin2. Gross deletions of this site decreased the state of phosphorylation of NHE5 as well as its binding and responsiveness to β-arrestin2 in intact cells. More refined in vitro analyses showed that this site was robustly phosphorylated by the acidotropic protein kinase CK2, whereas other kinases, such as CK1 or the GPCR kinase GRK2, were considerably less potent. Simultaneous mutation of five Ser/Thr residues within 702-714 to Ala ((702)ST/AA(714)) abolished phosphorylation and binding of β-arrestin2. In transfected cells, the CK2 catalytic α subunit formed a complex with NHE5 and decreased wild-type but not (702)ST/AA(714) NHE5 activity, further supporting a regulatory role for this kinase. The rate of internalization of (702)ST/AA(714) was also diminished and relatively insensitive to overexpression of β-arrestin2. However, unlike in vitro, this mutant retained its ability to form a complex with β-arrestin2 despite its lack of responsiveness. Additional mutations of two di-isoleucine-based motifs (I697A/L698A and I722A/I723A) that immediately flank the acidic cluster, either separately or together, were required to disrupt their association. These data demonstrate that discrete elements of an elaborate sorting signal in NHE5 contribute to β-arrestin2 binding and trafficking along the recycling endosomal pathway.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

