Do cell junction protein mutations cause an airway phenotype in mice or humans?
- PMID: 21297078
- PMCID: PMC3175552
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0498TR
Do cell junction protein mutations cause an airway phenotype in mice or humans?
Abstract
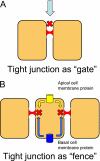
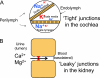
Cell junction proteins connect epithelial cells to each other and to the basement membrane. Genetic mutations of these proteins can cause alterations in some epithelia leading to varied phenotypes such as deafness, renal disease, skin disorders, and cancer. This review examines if genetic mutations in these proteins affect the function of lung airway epithelia. We review cell junction proteins with examples of disease mutation phenotypes in humans and in mouse knockout models. We also review which of these genes are expressed in airway epithelium by microarray expression profiling and immunocytochemistry. Last, we present a comprehensive literature review to find the lung phenotype when cell junction and adhesion genes are mutated or subject to targeted deletion. We found that in murine models, targeted deletion of cell junction and adhesion genes rarely result in a lung phenotype. Moreover, mutations in these genes in humans have no obvious lung phenotype. Our research suggests that simply because a cell junction or adhesion protein is expressed in an organ does not imply that it will exhibit a drastic phenotype when mutated. One explanation is that because a functioning lung is critical to survival, redundancy in the system is expected. Therefore mutations in a single gene might be compensated by a related function of a similar gene product. Further studies in human and animal models will help us understand the overlap in the function of cell junction gene products. Finally, it is possible that the human lung phenotype is subtle and has not yet been described.
Figures


References
-
- Schaedel C, Marthinsen L, Kristoffersson AC, Kornfalt R, Nilsson KO, Orlenius B, Holmberg L. Lung symptoms in pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 are associated with deficiency of the alpha-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. J Pediatr 1999;135:739–745. - PubMed
-
- Cereijido M, Contreras RG, Flores-Benítez D, Flores-Maldonado C, Larre I, Ruiz A, Shoshani L. New diseases derived or associated with the tight junction. Arch Med Res 2007;38:465–478. - PubMed
-
- Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 2006;68:403–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

