Targeting SET/I(2)PP2A oncoprotein functions as a multi-pathway strategy for cancer therapy
- PMID: 21297667
- PMCID: PMC3107340
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.622
Targeting SET/I(2)PP2A oncoprotein functions as a multi-pathway strategy for cancer therapy
Abstract
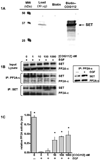
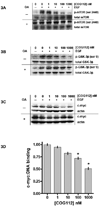
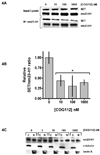
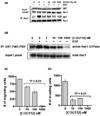
The SET oncoprotein participates in cancer progression by affecting multiple cellular processes, inhibiting the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and inhibiting the metastasis suppressor nm23-H1. On the basis of these multiple activities, we hypothesized that targeted inhibition of SET would have multiple discrete and measurable effects on cancer cells. Here, the effects of inhibiting SET oncoprotein function on intracellular signaling and proliferation of human cancer cell lines was investigated. We observed the effects of COG112, a novel SET interacting peptide, on PP2A activity, Akt signaling, nm23-H1 activity and cellular migration/invasion in human U87 glioblastoma and MDA-MB-231 breast adenocarcinoma cancer cell lines. We found that COG112 interacted with SET protein and inhibited the association between SET and PP2A catalytic subunit (PP2A-c) and nm23-H1. The interaction between COG112 and SET caused PP2A phosphatase and nm23-H1 exonuclease activities to increase. COG112-mediated increases in PP2A activity resulted in the inhibition of Akt signaling and cellular proliferation. Additionally, COG112 inhibited SET association with Ras-related C(3) botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), leading to decreased cellular migration and invasion. COG112 treatment releases the SET-mediated inhibition of the tumor suppressor PP2A, as well as the metastasis suppressor nm23-H1. These results establish SET as a novel molecular target and that the inhibition of SET may have beneficial effects in cancer chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Michael P. Vitek and Dale J. Christensen are stockholders in Cognosci, Inc., which has patent rights on a reagent used in this study. The remaining authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Adachi Y, Pavlakis GN, Copeland TD. Identification and characterization of SET, a nuclear phosphoprotein encoded by the translocation break point in acute undifferentiated leukemia. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:2258–2262. - PubMed
-
- Canela N, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Estanyol JM, Diaz C, Pujol MJ, Agell N, et al. The SET protein regulates G2/M transition by modulating cyclin B-cyclin-dependent kinase 1 activity. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1158–1164. - PubMed
-
- Carlson SG, Eng E, Kim EG, Perlman EJ, Copeland TD, Ballermann BJ. Expression of SET, an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A, in renal development and Wilms' tumor. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:1873–1880. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

