PDE 7 inhibitors: new potential drugs for the therapy of spinal cord injury
- PMID: 21297958
- PMCID: PMC3031524
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015937
PDE 7 inhibitors: new potential drugs for the therapy of spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background: Primary traumatic mechanical injury to the spinal cord (SCI) causes the death of a number of neurons that to date can neither be recovered nor regenerated. During the last years our group has been involved in the design, synthesis and evaluation of PDE7 inhibitors as new innovative drugs for several neurological disorders. Our working hypothesis is based on two different facts. Firstly, neuroinflammation is modulated by cAMP levels, thus the key role for phosphodiesterases (PDEs), which hydrolyze cAMP, is undoubtedly demonstrated. On the other hand, PDE7 is expressed simultaneously on leukocytes and on the brain, highlighting the potential crucial role of PDE7 as drug target for neuroinflammation.
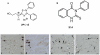
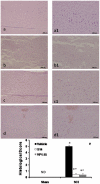
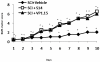
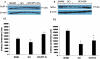
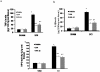
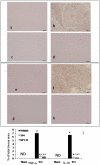
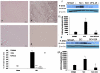
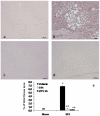
Methodology/principal findings: Here we present two chemically diverse families of PDE7 inhibitors, designed using computational techniques such as virtual screening and neuronal networks. We report their biological profile and their efficacy in an experimental SCI model induced by the application of vascular clips (force of 24 g) to the dura via a four-level T5-T8 laminectomy. We have selected two candidates, namely S14 and VP1.15, as PDE7 inhibitors. These compounds increase cAMP production both in macrophage and neuronal cell lines. Regarding drug-like properties, compounds were able to cross the blood brain barrier using parallel artificial membranes (PAMPA) methodology. SCI in mice resulted in severe trauma characterized by edema, neutrophil infiltration, and production of a range of inflammatory mediators, tissue damage, and apoptosis. Treatment of the mice with S14 and VP1.15, two PDE7 inhibitors, significantly reduced the degree of spinal cord inflammation, tissue injury (histological score), and TNF-α, IL-6, COX-2 and iNOS expression.
Conclusions/significance: All these data together led us to propose PDE7 inhibitors, and specifically S14 and VP1.15, as potential drug candidates to be further studied for the treatment of SCI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
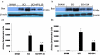
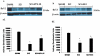

References
-
- Maegele M, Gregor S, Steinhausen E, Bouillon B, Heiss MM, et al. The long-distance tertiary air transfer and care of tsunami victims: injury pattern and microbiological and psychological aspects. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:1136–1140. - PubMed
-
- Bartholdi D, Schwab ME. Methylprednisolone inhibits early inflammatory processes but not ischemic cell death after experimental spinal cord lesion in the rat. Brain Res. 1995;672:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Levy ML, Chen JC, Amar AP, Yamada S, Togo K, et al. Virtual endoscopic environments in modern neurosurgical practice. Neurosurg Focus. 1999;6:e11. - PubMed
-
- Carlson SL, Parrish ME, Springer JE, Doty K, Dossett L. Acute inflammatory response in spinal cord following impact injury. Exp Neurol. 1998;151:77–88. - PubMed
-
- de Castro R, Hughes MG, Xu GY, Clifton C, Calingasan NY, et al. Evidence that infiltrating neutrophils do not release reactive oxygen species in the site of spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2004;190:414–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

