Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional reprogramming in mouse models of acute myeloid leukaemia
- PMID: 21297973
- PMCID: PMC3030562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016330
Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional reprogramming in mouse models of acute myeloid leukaemia
Abstract
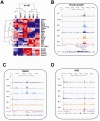
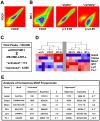
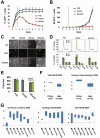
Acute leukaemias are commonly caused by mutations that corrupt the transcriptional circuitry of haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. However, the mechanisms underlying large-scale transcriptional reprogramming remain largely unknown. Here we investigated transcriptional reprogramming at genome-scale in mouse retroviral transplant models of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) using both gene-expression profiling and ChIP-sequencing. We identified several thousand candidate regulatory regions with altered levels of histone acetylation that were characterised by differential distribution of consensus motifs for key haematopoietic transcription factors including Gata2, Gfi1 and Sfpi1/Pu.1. In particular, downregulation of Gata2 expression was mirrored by abundant GATA motifs in regions of reduced histone acetylation suggesting an important role in leukaemogenic transcriptional reprogramming. Forced re-expression of Gata2 was not compatible with sustained growth of leukaemic cells thus suggesting a previously unrecognised role for Gata2 in downregulation during the development of AML. Additionally, large scale human AML datasets revealed significantly higher expression of GATA2 in CD34+ cells from healthy controls compared with AML blast cells. The integrated genome-scale analysis applied in this study represents a valuable and widely applicable approach to study the transcriptional control of both normal and aberrant haematopoiesis and to identify critical factors responsible for transcriptional reprogramming in human cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Melnick AM, Adelson K, Licht JD. The theoretical basis of transcriptional therapy of cancer: can it be put into practice? J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3957–3970. - PubMed
-
- Rabbitts TH. Chromosomal translocations in human cancer. Nature. 1994;372:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Look AT. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science. 1997;278:1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy JA, Barabe F. Investigating human leukemogenesis: from cell lines to in vivo models of human leukemia. Leukemia. 2008;22:2029–2040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

