The nuclear transcription factor PKNOX2 is a candidate gene for substance dependence in European-origin women
- PMID: 21298047
- PMCID: PMC3029286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016002
The nuclear transcription factor PKNOX2 is a candidate gene for substance dependence in European-origin women
Abstract
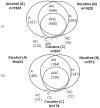
Substance dependence or addiction is a complex environmental and genetic disorder that results in serious health and socio-economic consequences. Multiple substance dependence categories together, rather than any one individual addiction outcome, may explain the genetic variability of such disorder. In our study, we defined a composite substance dependence phenotype derived from six individual diagnoses: addiction to nicotine, alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, opiates or other drugs as a whole. Using data from several genomewide case-control studies, we identified a strong (Odds ratio = 1.77) and significant (p-value = 7E-8) association signal with a novel gene, PBX/knotted 1 homeobox 2 (PKNOX2), on chromosome 11 with the composite phenotype in European-origin women. The association signal is not as significant when individual outcomes for addiction are considered, or in males or African-origin population. Our findings underscore the importance of considering multiple addiction types and the importance of considering population and gender stratification when analyzing data with heterogeneous population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) State-specific smoking-attributable mortality and years of potential life lost–United States, 2000-2004. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:29–33. - PubMed
-
- Makhija NJ, Sher L. Preventing suicide in adolescents with alcohol use disorders. Int J Adolesc Med Health. 2007;19:53–59. - PubMed
-
- Uhl GR, Elmer GI, Lanuda MC, Pickens RW. Genetic influences in drug abuse. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ, editors. Psychopharmacology: The Fourth Generation of Progress. New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1995. pp. 1793–1806.
-
- True WR, Heath AC, Scherrer JF, Xian H, Lin N, et al. Interrelationship of genetic and environmental influences on conduct disorder and alcohol and marijuana dependence symptoms. Am J Med Genet. 1999;88:391–397. - PubMed
-
- Merikangas KR, Stolar M, Stevens DE, Goulet J, Preisig MA, et al. Familial transmission of substance use disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:973–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016750/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013423/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA017713/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K02DA017713/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH014235/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA016750/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials