Assessing conservation values: biodiversity and endemicity in tropical land use systems
- PMID: 21298054
- PMCID: PMC3029302
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016238
Assessing conservation values: biodiversity and endemicity in tropical land use systems
Abstract
Despite an increasing amount of data on the effects of tropical land use on continental forest fauna and flora, it is debatable whether the choice of the indicator variables allows for a proper evaluation of the role of modified habitats in mitigating the global biodiversity crisis. While many single-taxon studies have highlighted that species with narrow geographic ranges especially suffer from habitat modification, there is no multi-taxa study available which consistently focuses on geographic range composition of the studied indicator groups. We compiled geographic range data for 180 bird, 119 butterfly, 204 tree and 219 understorey plant species sampled along a gradient of habitat modification ranging from near-primary forest through young secondary forest and agroforestry systems to annual crops in the southwestern lowlands of Cameroon. We found very similar patterns of declining species richness with increasing habitat modification between taxon-specific groups of similar geographic range categories. At the 8 km(2) spatial level, estimated richness of endemic species declined in all groups by 21% (birds) to 91% (trees) from forests to annual crops, while estimated richness of widespread species increased by +101% (trees) to +275% (understorey plants), or remained stable (-2%, butterflies). Even traditional agroforestry systems lost estimated endemic species richness by -18% (birds) to -90% (understorey plants). Endemic species richness of one taxon explained between 37% and 57% of others (positive correlations) and taxon-specific richness in widespread species explained up to 76% of variation in richness of endemic species (negative correlations). The key implication of this study is that the range size aspect is fundamental in assessments of conservation value via species inventory data from modified habitats. The study also suggests that even ecologically friendly agricultural matrices may be of much lower value for tropical conservation than indicated by mere biodiversity value.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
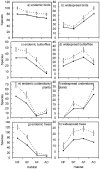
References
-
- Lawton JH, Bignell DE, Bolton B, Bloemers GF, Eggleton P, et al. Biodiversity inventories, indicator taxa and effects of habitat modification in tropical forest. Nature. 1998;391:72–76.
-
- Schulze CH, Waltert M, Kessler P, Pitopang R, Shahabuddin, et al. Biodiversity indicator groups of tropical land use systems: comparing plants, birds, and insects. Ecol Appl. 2004;14:1321–1333.
-
- Perfecto I, Mas A, Dietsch T, Vandermeer J. Conservation of biodiversity in coffee agroecosystems: a tri-taxa comparison in southern Mexico. Biodivers Conserv. 2003;12:1239–1252.
-
- Pardini R, Faria D, Accacio GM, Laps RR, Mariano-neto E, et al. The challenge of maintaining Atlantic forest biodiversity: A multi-taxa conservation assessment of specialist and generalist species in an agro-forestry mosaic in southern Bahia. Biol Conserv. 2009;142:1178–1190. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2009.02.010. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

