High-dose enalapril treatment reverses myocardial fibrosis in experimental uremic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 21298056
- PMCID: PMC3029304
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015287
High-dose enalapril treatment reverses myocardial fibrosis in experimental uremic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Aims: Patients with renal failure develop cardiovascular alterations which contribute to the higher rate of cardiac death. Blockade of the renin angiotensin system ameliorates the development of such changes. It is unclear, however, to what extent ACE-inhibitors can also reverse existing cardiovascular alterations. Therefore, we investigated the effect of high dose enalapril treatment on these alterations.
Methods: Male Sprague Dawley rats underwent subtotal nephrectomy (SNX, n = 34) or sham operation (sham, n = 39). Eight weeks after surgery, rats were sacrificed or allocated to treatment with either high-dose enalapril, combination of furosemide/dihydralazine or solvent for 4 weeks. Heart and aorta were evaluated using morphometry, stereological techniques and TaqMan PCR.
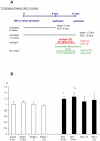
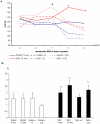
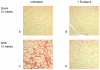
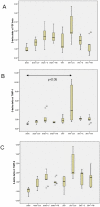
Results: After 8 and 12 weeks systolic blood pressure, albumin excretion, and left ventricular weight were significantly higher in untreated SNX compared to sham. Twelve weeks after SNX a significantly higher volume density of cardiac interstitial tissue (2.57±0.43% in SNX vs 1.50±0.43% in sham, p<0.05) and a significantly lower capillary length density (4532±355 mm/mm(3) in SNX vs 5023±624 mm/mm(3) in sham, p<0.05) were found. Treatment of SNX with enalapril from week 8-12 significantly improved myocardial fibrosis (1.63±0.25%, p<0.05), but not capillary reduction (3908±486 mm/mm(3)) or increased intercapillary distance. In contrast, alternative antihypertensive treatment showed no such effect. Significantly increased media thickness together with decreased vascular smooth muscles cell number and a disarray of elastic fibres were found in the aorta of SNX animals compared to sham. Both antihypertensive treatments failed to cause complete regression of these alterations.
Conclusions: The study indicates that high dose ACE-I treatment causes partial, but not complete, reversal of cardiovascular changes in SNX.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Amann K, Ritz E. Cardiac disease in chronic uremia: Pathophysiology. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 1997;4:212–224. - PubMed
-
- Mall G, Rambausek M, Neumeister A, Kollmar S, Vetterlein F, et al. Myocardial interstitial fibrosis in experimental uremia – implications for cardiac compliance. Kidney Int. 1988;33:804–811. - PubMed
-
- Amann K, Ritz E, Wiest G, Klaus G, Mall G. A role of parathyroid hormone for the activation of cardiac fibroblasts in uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994;4:1814–1819. - PubMed
-
- Amann K, Tyralla K, Gross ML, Schwarz U, Törnig J, et al. Cardiomyocyte loss in experimental renal failure: Prevention by ramipril. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1708–1713. - PubMed
-
- Amann K, Neusuess R, Ritz E, Irzyniec T, Wiest G, et al. Changes of vascular architecture independent of blood pressure in experimental renal failure. Am J Hypertens. 1995;8:409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

