RNF12 activates Xist and is essential for X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 21298085
- PMCID: PMC3029249
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002001
RNF12 activates Xist and is essential for X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
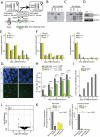
In somatic cells of female placental mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is transcriptionally silenced to accomplish an equal dose of X-encoded gene products in males and females. Initiation of random X chromosome inactivation (XCI) is thought to be regulated by X-encoded activators and autosomally encoded suppressors controlling Xist. Spreading of Xist RNA leads to silencing of the X chromosome in cis. Here, we demonstrate that the dose dependent X-encoded XCI activator RNF12/RLIM acts in trans and activates Xist. We did not find evidence for RNF12-mediated regulation of XCI through Tsix or the Xist intron 1 region, which are both known to be involved in inhibition of Xist. In addition, we found that Xist intron 1, which contains a pluripotency factor binding site, is not required for suppression of Xist in undifferentiated ES cells. Analysis of female Rnf12⁻/⁻ knockout ES cells showed that RNF12 is essential for initiation of XCI and is mainly involved in the regulation of Xist. We conclude that RNF12 is an indispensable factor in up-regulation of Xist transcription, thereby leading to initiation of random XCI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Lyon MF. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961;190:372–373. - PubMed
-
- Takagi N, Sasaki M. Preferential inactivation of the paternally derived X chromosome in the extraembryonic membranes of the mouse. Nature. 1975;256:640–642. - PubMed
-
- Huynh KD, Lee JT. Inheritance of a pre-inactivated paternal X chromosome in early mouse embryos. Nature. 2003;426:857–862. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto I, Otte AP, Allis CD, Reinberg D, Heard E. Epigenetic dynamics of imprinted X inactivation during early mouse development. Science. 2004;303:644–649. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N, Ashworth A, Kay GF, McCabe VM, Norris DP, et al. The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell. 1992;71:515–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

