Structure-activity relationships in nucleotide oligomerization domain 1 (Nod1) agonistic γ-glutamyldiaminopimelic acid derivatives
- PMID: 21299227
- PMCID: PMC3076632
- DOI: 10.1021/jm101535e
Structure-activity relationships in nucleotide oligomerization domain 1 (Nod1) agonistic γ-glutamyldiaminopimelic acid derivatives
Abstract
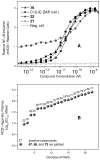
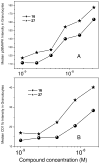
N-acyl-γ-glutamyldiaminopimelic acid is a prototype ligand for Nod1. We report a detailed SAR of C(12)-γ-D-Glu-DAP. Analogues with glutaric or γ-aminobutyric acid replacing the glutamic acid show greatly attenuated Nod1-agonistic activity. Substitution of the meso-diaminopimelic (DAP) acid component with monoaminopimelic acid, L- or D-lysine, or cadaverine also results in reduced activity. The free amine on DAP is crucial. However, the N-acyl group on the D-glutamyl residue can be substituted with N-alkyl groups with full preservation of activity. The free carboxylates on the DAP and Glu components can also be esterified, resulting in more lipophilic but active analogues. Transcriptomal profiling showed a dominant up-regulation of IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, and IL-24, which may explain the pronounced Th2-polarizing activity of these compounds and also implicate cell signaling mediated by TREM-1. These results may explain the hitherto unknown mechanism of synergy between Nod1 and TLR agonists and are likely to be useful in designing vaccine adjuvants.
Figures



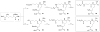
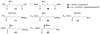

References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Semin Immunol. 2007;19:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai Y, Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pathogen recognition by innate receptors. J Infect Chemother. 2008;14:86–92. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai Y, Akira S. Identification and functions of pattern-recognition receptors. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:985–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

