Cellular changes in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis
- PMID: 21300066
- PMCID: PMC3081914
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.046
Cellular changes in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis
Abstract
Background & aims: Cellular changes associated with diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis are not well described. The aim of this study was to describe histologic abnormalities in gastroparesis and compare findings in idiopathic versus diabetic gastroparesis.
Methods: Full-thickness gastric body biopsy specimens were obtained from 40 patients with gastroparesis (20 diabetic) and matched controls. Sections were stained for H&E and trichrome and immunolabeled with antibodies against protein gene product (PGP) 9.5, neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P, and tyrosine hydroxylase to quantify nerves, S100β for glia, Kit for interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), CD45 and CD68 for immune cells, and smoothelin for smooth muscle cells. Tissue was also examined by transmission electron microscopy.
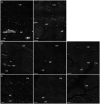
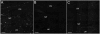
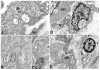
Results: Histologic abnormalities were found in 83% of patients. The most common defects were loss of ICC with remaining ICC showing injury, an abnormal immune infiltrate containing macrophages, and decreased nerve fibers. On light microscopy, no significant differences were found between diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis with the exception of nNOS expression, which was decreased in more patients with idiopathic gastroparesis (40%) compared with diabetic patients (20%) by visual grading. On electron microscopy, a markedly increased connective tissue stroma was present in both disorders.
Conclusions: This study suggests that on full-thickness biopsy specimens, cellular abnormalities are found in the majority of patients with gastroparesis. The most common findings were loss of Kit expression, suggesting loss of ICC, and an increase in CD45 and CD68 immunoreactivity. These findings suggest that examination of tissue can lead to valuable insights into the pathophysiology of these disorders and offer hope that new therapeutic targets can be found.
Copyright © 2011 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Park MI, Camilleri M. Gastroparesis: clinical update. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1129–39. - PubMed
-
- Parkman HP, Hasler WL, Fisher RS, et al. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1592–622. - PubMed
-
- Pasricha PJ. The riddle, mystery, and enigma of gastroparesis. J Support Oncol. 2007;5:368–70. - PubMed
-
- Patrick A, Epstein O. Review article: gastroparesis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:724–40. - PubMed
-
- Vittal H, Farrugia G, Gomez G, et al. Mechanisms of disease: the pathological basis of gastroparesis--a review of experimental and clinical studies. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;4:336–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01DK073975/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK074008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057061/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073975/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK074035/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK074008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK073983/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK073985/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK073974/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK068055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK074007/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK68055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073985/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK074007/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57061/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK073974/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK084567/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

