Kids and adults now! Defeat Obesity (KAN-DO): rationale, design and baseline characteristics
- PMID: 21300177
- PMCID: PMC3087307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2011.01.017
Kids and adults now! Defeat Obesity (KAN-DO): rationale, design and baseline characteristics
Abstract
Background: Prevention of childhood obesity is a public health priority. Parents influence a child's weight by modeling healthy behaviors, controlling food availability and activity opportunities, and appropriate feeding practices. Thus interventions should target education and behavioral change in the parent, and positive, mutually reinforcing behaviors within the family.
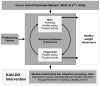
Methods: This paper presents the design, rationale and baseline characteristics of Kids and Adults Now! - Defeat Obesity (KAN-DO), a randomized controlled behavioral intervention trial targeting weight maintenance in children of healthy weight, and weight reduction in overweight children. 400 children aged 2-5 and their overweight or obese mothers in the Triangle and Triad regions of North Carolina are randomized equally to control or the KAN-DO intervention, consisting of mailed family kits encouraging healthy lifestyle change. Eight (monthly) kits are supported by motivational counseling calls and a single group session. Mothers are targeted during a hypothesized "teachable moment" for health behavior change (the birth of a new baby), and intervention content addresses: parenting skills ((e.g., emotional regulation, authoritative parenting), healthy eating, and physical activity.
Results: The 400 mother-child dyads randomized to trial are 75% white and 22% black; 19% have a household income of $30,000 or below. At baseline, 15% of children are overweight (85th-95th percentile for body mass index) and 9% are obese (≥ 95th percentile).
Conclusion: This intervention addresses childhood obesity prevention by using a family-based, synergistic approach, targeting at-risk children and their mothers during key transitional periods, and enhancing maternal self-regulation and responsive parenting as a foundation for health behavior change.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Lamb MM, Flegal KM. Prevalence of high body mass index in US children and adolescents, 2007–2008. JAMA. 2010;303(3):242–9. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine. Preventing Childhood Obesity: Health in the Balance. Washington D.C: National Academies Press; 2005. - PubMed
-
- Barlow SE, Dietz WH. Obesity evaluation and treatment: Expert Committee recommendations. The Maternal and Child Health Bureau, Health Resources and Services Administration and the Department of Health and Human Services. Pediatrics. 1998;102(3):E29. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(13):869–73. - PubMed
-
- Golan M, Crow S. Parents are key players in the prevention and treatment of weight-related problems. Nutrition Reviews. 2004;62(1):39–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical