The effects of thrombin and cytokines upon the biomechanics and remodeling of isolated amnion membrane, in vitro
- PMID: 21300402
- PMCID: PMC3049450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.01.006
The effects of thrombin and cytokines upon the biomechanics and remodeling of isolated amnion membrane, in vitro
Abstract
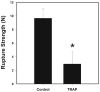
Abruption-induced thrombin generation and inflammation/infection induced cytokine production have both been associated with fetal membrane (FM) weakening and preterm premature rupture of the fetal membranes (PPROM). Using our in vitro model system we have demonstrated that thrombin, and separately the cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) and interleukin-1-beta (IL-1β), remodel and weaken full thickness FM. Additionally, we have reported that the anti-oxidant and NFκB inhibitor, alpha-lipoic acid (LA), blocks these thrombin and cytokine induced effects. The purpose of these studies was to determine whether thrombin and cytokines directly weaken the amnion membrane (AM), the major load-bearing component of FM. Isolated AM or full thickness FM fragments from unlabored Cesarean deliveries were incubated with thrombin, TNFα, or IL-1β, for 48 h. Rupture strength (breaking force) of each fragment was thereafter determined using our published methodology. Biochemical evidence of remodeling and apoptosis; immunoreactive Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP3) and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (C-PARP) levels in tissue extracts, were determined by western blot and densitometry. Thrombin induced a dose-dependent weakening of isolated AM (P < 0.001) coupled with dose dependent increases in PARP cleavage, and reciprocal increases and decreases, respectively, in MMP9 and TIMP3 protein (all P < 0.01). Thrombin receptor activating peptide-6 (TRAP) also weakened isolated AM. Neither TNFα nor IL-1β weakened isolated AM. However, both cytokines weakened AM when it was incubated together with the choriodecidua as part of full thickness FM (P < 0.001). Cytokine-conditioned choriodecidua medium also weakened isolated AM (P < 0.001). Under conditions in which cytokines weakened the AM, the changes in MMP9, TIMP3 and PARP cleavage were consistent with those seen after thrombin incubation. LA blocked the FM weakening and remodeling effects. In summary, thrombin weakens AM directly whereas cytokines weaken AM indirectly by causing the release of soluble intermediates from the choriodecidua.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures












References
-
- Mercer BM. Premature Rupture of the membranes. An expert’s view. Obstet G ynecol. 2003;101:178–93. - PubMed
-
- Menon R. Spontaneous preterm birth, a clinical dilemma: etiologic, pathophysiologic and genetic heterogeneities and racial disparity. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87:590–600. - PubMed
-
- Parry S, Strauss JF. Premature rupture of the fetal membranes. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:663–70. - PubMed
-
- Menon R, Fortunato SJ. The role of matrix degrading enzymes and apoptosis in rupture of membranes. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2004;11:427–37. - PubMed
-
- Moore RM, Mansour JM, Redline RW, Mercer BM, Moore JJ. The physiology of fetal membrane rupture: insight gained from the determination of physical properties. Placenta. 2006;27:1037–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

