Pharmacokinetics of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors: the role of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein binding
- PMID: 21300760
- PMCID: PMC3703823
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2736
Pharmacokinetics of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors: the role of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein binding
Abstract
Purpose: In a phase I trial for patients with refractory solid tumors, hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) showed little decline in plasma concentrations over 7 days after a single oral dose and nonlinearity with respect to dose and time after single and multiple dosing. We studied the role of GDC-0449 binding to plasma protein alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) to better understand these unusual pharmacokinetics.
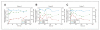
Experimental design: Sixty-eight patients received GDC-0449 at 150 (n = 41), 270 (n = 23), or 540 (n = 4) mg/d, with pharmacokinetic (PK) sampling at multiple time points. Total and unbound (dialyzed) GDC-0449 plasma concentrations were assessed by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry, binding kinetics by surface plasmon resonance-based microsensor, and AAG levels by ELISA.
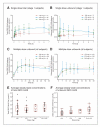
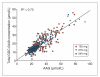
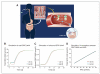
Results: A linear relationship between total GDC-0449 and AAG plasma concentrations was observed across dose groups (R(2) = 0.73). In several patients, GDC-0449 levels varied with fluctuations in AAG levels over time. Steady-state, unbound GDC-0449 levels were less than 1% of total, independent of dose or total plasma concentration. In vitro, GDC-0449 binds AAG strongly and reversibly (K(D) = 13 μmol/L) and human serum albumin less strongly (K(D) = 120 μmol/L). Simulations from a derived mechanistic PK model suggest that GDC-0449 pharmacokinetics are mediated by AAG binding, solubility-limited absorption, and slow metabolic elimination.
Conclusions: GDC-0449 levels strongly correlated with AAG levels, showing parallel fluctuations of AAG and total drug over time and consistently low, unbound drug levels, different from previously reported AAG-binding drugs. This PK profile is due to high-affinity, reversible binding to AAG and binding to albumin, in addition to solubility-limited absorption and slow metabolic elimination properties.
©2011 AACR.
Figures

Comment in
-
Targeting the Hedgehog pathway in cancer: can the spines be smoothened?Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 15;17(8):2071-3. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0211. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21367749
References
-
- Scales SJ, de Sauvage FJ. Mechanisms of hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:303–12. - PubMed
-
- Hahn H, Christiansen J, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulos PG, Chidambaram A, Gerrard B, et al. A mammalian patched homolog is expressed in target tissues of sonic hedgehog and maps to a region associated with developmental abnormalities. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12125–8. - PubMed
-
- Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM, et al. Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science. 1996;272:1668–71. - PubMed
-
- Pietsch T, Waha A, Koch A, Kraus J, Albrecht S, Tonn J, et al. Medulloblastomas of the desmoplastic variant carry mutations of the human homologue of Drosophila patched. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2085–8. - PubMed
-
- Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, Hebrink D, Alderete B, Fults DW, et al. Sporadic medulloblastomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res. 1997;57:842–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

