Mechanistic and structural insights into the regioselectivity of an acyl-CoA fatty acid desaturase via directed molecular evolution
- PMID: 21300802
- PMCID: PMC3075633
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.191098
Mechanistic and structural insights into the regioselectivity of an acyl-CoA fatty acid desaturase via directed molecular evolution
Abstract
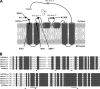
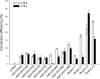
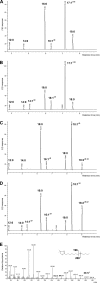
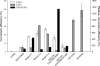
Membrane-bound fatty acid desaturases and related enzymes play a pivotal role in the biosynthesis of unsaturated and various unusual fatty acids. Structural insights into the remarkable catalytic diversity and wide range of substrate specificities of this class of enzymes remain limited due to the lack of a crystal structure. To investigate the structural basis of the double bond positioning (regioselectivity) of the desaturation reaction in more detail, we relied on a combination of directed evolution in vitro and a powerful yeast complementation assay to screen for Δx regioselectivity. After two selection rounds, variants of the bifunctional Δ12/Δ9-desaturase from the house cricket (Acheta domesticus) exhibited increased Δ9-desaturation activity on shorter chain fatty acids. This change in specificity was the result of as few as three mutations, some of them near the putative active site. Subsequent analysis of individual substitutions revealed an important role of residue Phe-52 in facilitating Δ9-desaturation of shorter chain acyl substrates and allowed for the redesign of the cricket Δ12/Δ9-desaturase into a 16:0-specific Δ9-desaturase. Our results demonstrate that a minimal number of mutations can have a profound impact on the regioselectivity of acyl-CoA fatty acid desaturases and include the first biochemical data supporting the acyl-CoA acyl carrier specificity of a desaturase able to carry out Δ12-desaturation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Desaturases: Structural and mechanistic insights into the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids.IUBMB Life. 2022 Nov;74(11):1036-1051. doi: 10.1002/iub.2671. Epub 2022 Sep 18. IUBMB Life. 2022. PMID: 36017969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A conserved evolutionary mechanism permits Δ9 desaturation of very-long-chain fatty acyl lipids.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 7;295(32):11337-11345. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014258. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32527722 Free PMC article.
-
Two clusters of residues contribute to the activity and substrate specificity of Fm1, a bifunctional oleate and linoleate desaturase of fungal origin.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 21;293(51):19844-19853. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005972. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30348899 Free PMC article.
-
Structure determinants for the substrate specificity of acyl-CoA Δ9 desaturases from a marine copepod.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):922-34. doi: 10.1021/cb400675d. Epub 2014 Jan 29. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24475735
-
Structure and Function of Δ9-Fatty Acid Desaturase.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019;67(4):327-332. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-01001. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 30930436 Review.
Cited by
-
Desaturase specificity is controlled by the physicochemical properties of a single amino acid residue in the substrate binding tunnel.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 May 14;18:1202-1209. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.05.011. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32542106 Free PMC article.
-
Desaturases: Structural and mechanistic insights into the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids.IUBMB Life. 2022 Nov;74(11):1036-1051. doi: 10.1002/iub.2671. Epub 2022 Sep 18. IUBMB Life. 2022. PMID: 36017969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional desaturase Fads1 (Δ5) and Fads2 (Δ6) orthologues evolved before the origin of jawed vertebrates.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031950. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384110 Free PMC article.
-
ω3 fatty acid desaturases from microorganisms: structure, function, evolution, and biotechnological use.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Dec;97(24):10255-62. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5336-5. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24177732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of amino acid residues that determine the substrate specificity of mammalian membrane-bound front-end fatty acid desaturases.J Lipid Res. 2016 Jan;57(1):89-99. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M064121. Epub 2015 Nov 20. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26590171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guy J. E., Whittle E., Kumaran D., Lindqvist Y., Shanklin J. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 19863–19871 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

