Aire-dependent production of XCL1 mediates medullary accumulation of thymic dendritic cells and contributes to regulatory T cell development
- PMID: 21300913
- PMCID: PMC3039864
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20102327
Aire-dependent production of XCL1 mediates medullary accumulation of thymic dendritic cells and contributes to regulatory T cell development
Abstract
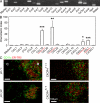
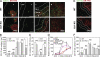
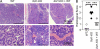
Dendritic cells (DCs) in the thymus (tDCs) are predominantly accumulated in the medulla and contribute to the establishment of self-tolerance. However, how the medullary accumulation of tDCs is regulated and involved in self-tolerance is unclear. We show that the chemokine receptor XCR1 is expressed by tDCs, whereas medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) express the ligand XCL1. XCL1-deficient mice are defective in the medullary accumulation of tDCs and the thymic generation of naturally occurring regulatory T cells (nT reg cells). Thymocytes from XCL1-deficient mice elicit dacryoadenitis in nude mice. mTEC expression of XCL1, tDC medullary accumulation, and nT reg cell generation are diminished in Aire-deficient mice. These results indicate that the XCL1-mediated medullary accumulation of tDCs contributes to nT reg cell development and is regulated by Aire.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

