New hydrophilic/lipophilic tetra-α-(4-carboxyphenoxy) phthalocyanine zinc-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402 cells by triggering apoptosis and arresting cell cycle
- PMID: 21301411
- PMCID: PMC6259621
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules16021389
New hydrophilic/lipophilic tetra-α-(4-carboxyphenoxy) phthalocyanine zinc-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402 cells by triggering apoptosis and arresting cell cycle
Abstract
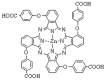
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a novel and promising antitumor treatment. Phthalocyanine-mediated PDT has shown antitumor activity in some tumor cells, but the effect of new hydrophilic/lipophilic tetra-α-(4-carboxyphenoxy)phthalocyanine zinc (TαPcZn)-mediated PDT (TαPcZn-PDT) on human hepatocellular carcinoma Bel-7402 cells and underlying mechanisms have not been clarified. In the present study, therefore, the ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectrum and cellular localization of TαPcZn, and effect of TαPcZn-PDT on the proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, Bcl-2 and Fas in Bel-7402 cells were investigated by spectrophotometry, inverted microscope, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, electron microscopy, annexinV-FITC/propidium iodide double staining, DNA content and immunoblot assay, respectively. We found that an intense absorption in UV-vis absorption spectrum of TαPcZn was in the red visible region at 650-680 nm, where light penetration in tissue is efficient, that green TαPcZn localized to both plasma membrane and nuclear membrane of Bel-7402 cells, signifying that there was a selective uptake of TαPcZn in Bel-7402 cells and TαPcZn-PDT would be expected to directly damage DNA, and that TαPcZn-PDT significantly resulted in the proliferation inhibition, apoptosis induction, S cell cycle arrest, and down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Fas. Taken together, we conclude that TαPcZn-PDT inhibits the proliferation of Bel-7402 cells by triggering apoptosis and arresting the cell cycle.
Figures






References
-
- Xia C.H., Wang B.Q., Wang Y., Liu Y.Q., Xu G.Y., Wu S. Damaging effects of nanosized TiO2 on bel-7402 human liver cancer cell under photoinduce. J. Inorg. Mater. 2006;21:1467–1471.
-
- Gurba P., Vallinayagam R., Schmitt F., Furrer J., Juillerat-Jeanneret L., Neier R. Novel bioconjugates of aminolevulinic acid with nucleosides. Synthesis. 2008;24:3957–3962.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

