A role for glutamate in subjective response to smoking and its action on inhibitory control
- PMID: 21301814
- PMCID: PMC3111550
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-011-2189-4
A role for glutamate in subjective response to smoking and its action on inhibitory control
Abstract
Rationale: Our previous study using memantine in smokers suggests that there may be a differential role for N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in the subjective and cognitive effects of smoking.
Objectives: This study was designed to investigate if D-cycloserine (DCS) would modulate the subjective and cognitive effects of limited smoking.
Methods: Forty-eight habitual smokers abstinent for a minimum of 2 h were randomly allocated to receive either placebo or 50 mg DCS (double-blind) and were subsequently required either to smoke half of one cigarette or to remain abstinent. Subjective and physiological effects of DCS were measured at baseline, 90 min postcapsule, and again after the partial-smoking manipulation, while the effects on sustained attention (rapid visual information processing test--RVIP) and cognitive flexibility (intra-extra dimensional set-shift test--IED) were evaluated only after the partial-smoking manipulation.
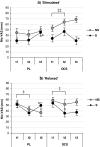
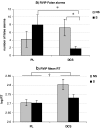
Results: DCS alone did not produce significant subjective effects other than an increase in ratings of "Stimulated". In combination with partial smoking, however, DCS blocked the smoking-induced increase in "Stimulated" and the decrease in "Relaxed" ratings. Furthermore, in combination with smoking, DCS reduced the number of false alarms during the RVIP test (an index of inhibitory control) and produced a small increase in diastolic blood pressure. DCS failed to modulate IED performance.
Conclusions: These findings provide further evidence of a role for glutamate release in the subjective effects of smoking but not the effects on attention and cognitive flexibility. Furthermore, our results indicate that glutamate release may also be involved in the effect of smoking on inhibitory control.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential involvement of glutamatergic mechanisms in the cognitive and subjective effects of smoking.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Jan;34(2):257-65. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.50. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18418361 Clinical Trial.
-
Absence of significant interactive effects of high-dose D-cycloserine and ethanol in healthy human subjects: preliminary insights into ethanol actions at the glycine B site of NMDA glutamate receptors.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 Jan;32(1):36-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00543.x. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008. PMID: 18028532
-
Cue exposure and response prevention with heavy smokers: a laboratory-based randomised placebo-controlled trial examining the effects of D-cycloserine on cue reactivity and attentional bias.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 May;221(2):273-84. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2571-2. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22101394 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of D-cycloserine on negative symptoms in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2004 Dec 1;71(2-3):239-48. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2004.03.013. Schizophr Res. 2004. PMID: 15474895 Review.
-
The Therapeutic Role of d-Cycloserine in Schizophrenia.Adv Pharmacol. 2016;76:39-66. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Adv Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27288073 Review.
Cited by
-
Do specific NMDA receptor subunits act as gateways for addictive behaviors?Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Jan;16(1):118-138. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12348. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 27706932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamate and synaptic plasticity systems and smoking behavior: results from a genetic association study.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038666. Epub 2012 Jun 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719919 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of varenicline on aspects of inhibitory control in smokers.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(18):3771-85. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3512-7. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24652107 Clinical Trial.
-
D-amino acid aberrations in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of smokers.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Sep;38(10):2019-26. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.103. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23615666 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of glutamatergic and GABAergic systems in nicotine dependence: Implications for novel pharmacotherapies for smoking cessation.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):554-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.042. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23752091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

