Cognitive effects of genetic variation in monoamine neurotransmitter systems: a population-based study of COMT, MAOA, and 5HTTLPR
- PMID: 21302344
- PMCID: PMC3494973
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31150
Cognitive effects of genetic variation in monoamine neurotransmitter systems: a population-based study of COMT, MAOA, and 5HTTLPR
Abstract
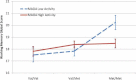
Individual differences in cognitive function are highly heritable and most likely driven by multiple genes of small effect. Well-characterized common functional polymorphisms in the genes MAOA, COMT, and 5HTTLPR each have predictable effects on the availability of the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin. We hypothesized that 5HTTLPR genotype would show little association with prefrontal cognitive performance, but that COMT and MAOA would have interacting effects on cognition through their shared influence on prefrontal catecholamine availability. We assessed the individual and epistatic effects of functional polymorphisms in COMT, MAOA, and 5HTTLPR on children's prefrontal cognitive function in nearly 6,000 children from the population-based Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Neither MAOA nor 5HTTLPR polymorphisms showed significant effects on cognitive function. In boys but not girls, there was a modest but statistically significant interaction between MAOA and COMT genotypes such that increased prefrontal catecholamine availability was associated with better working memory. These results suggest that assessment of multiple genes within functionally related systems may improve our understanding of the genetic basis of cognition.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS. Alpha 2-adrenergic mechanisms in prefrontal cortex associated with cognitive decline in aged nonhuman primates. Science. 1985;230:1273–1276. - PubMed
-
- Balciuniene J, Emilsson L, Oreland L, Pettersson U, Jazin E. Investigation of the functional effect of monoamine oxidase polymorphisms in human brain. Hum Genet. 2002;110:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JH, Heron J, Ring SM, Golding J, Goldman D, Xu K, Jones PB. Gender-specific effects of the catechol-O-methyltransferase Val108/158Met polymorphism on cognitive function in children. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:142–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

