Prevention of pulmonary complications of pneumoperitoneum in rats
- PMID: 21303502
- PMCID: PMC3044100
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8090-6-14
Prevention of pulmonary complications of pneumoperitoneum in rats
Abstract
Background: Carbon dioxide (CO2) pneumoperitoneum facilitates the visualization of abdominal organs during laparoscopic surgery. However, the associated increase in intra-abdominal pressure causes oxidative stress, which contributes to tissue injury.
Objective: We investigated the ability of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug Erdosteine to prevent CO2 pneumoperitoneum-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory reactions in a rat model.
Methods: Fourteen female adult Wistar albino rats were divided into a control group (Group A, n = 7) and an Erdosteine group (Group B, n = 7). Group A received 0.5 cc/day 0.9% NaCl, and Group B received 10 mg/kg/day Erdosteine was administered by gavage, and maintained for 7 days prior to the operation. During the surgical procedure, the rats were exposed to CO2 pneumoperitoneum with an intra-abdominal pressure of 15 mmHg for 30 min. The peritoneal gas was then desufflated. The rats were sacrificed following 3 h of insufflation. Their lungs were removed, histologically evaluated, and scored for intra-alveolar hemorrhage, alveolar edema, congestion, and leukocyte infiltration. The results were statistically analyzed. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Significant differences were detected in intra-alveolar hemorrhage (P < 0.05), congestion (P < 0.001), and leukocyte infiltration (P < 0.001) in Group A compared with Group B. However, the differences in alveolar edema were not statistically significant (P = 0.698).
Conclusions: CO2 pneumoperitoneum results in oxidative injury to lung tissue, and administration of Erdosteine reduces the severity of pathological changes. Therefore, Erdosteine may be a useful preventive and therapeutic agent for CO2 pneumoperitoneum-induced oxidative stress in laparoscopic surgery.
Figures
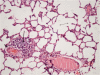
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

