Neuropathologic features in the hippocampus and cerebellum of three older men with fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 21303513
- PMCID: PMC3045897
- DOI: 10.1186/2040-2392-2-2
Neuropathologic features in the hippocampus and cerebellum of three older men with fragile X syndrome
Abstract
Background: Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the most common inherited form of intellectual disability, and is the most common single-gene disorder known to be associated with autism. Despite recent advances in functional neuroimaging and our understanding of the molecular pathogenesis, only limited neuropathologic information on FXS is available.
Methods: Neuropathologic examinations were performed on post-mortem brain tissue from three older men (aged 57, 64 and 78 years) who had received a clinical or genetic diagnosis of FXS. In each case, physical and cognitive features were typical of FXS, and one man was also diagnosed with autism. Guided by reports of clinical and neuroimaging abnormalities of the limbic system and cerebellum of individuals with FXS, the current analysis focused on neuropathologic features present in the hippocampus and the cerebellar vermis.
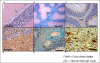
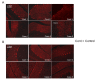
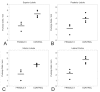
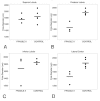
Results: Histologic and immunologic staining revealed abnormalities in both the hippocampus and cerebellar vermis. Focal thickening of hippocampal CA1 and irregularities in the appearance of the dentate gyrus were identified. All lobules of the cerebellar vermis and the lateral cortex of the posterior lobe of the cerebellum had decreased numbers of Purkinje cells, which were occasionally misplaced, and often lacked proper orientation. There were mild, albeit excessive, undulations of the internal granular cell layer, with patchy foliar white matter axonal and astrocytic abnormalities. Quantitative analysis documented panfoliar atrophy of both the anterior and posterior lobes of the vermis, with preferential atrophy of the posterior lobule (VI to VII) compared with age-matched normal controls.
Conclusions: Significant morphologic changes in the hippocampus and cerebellum in three adult men with FXS were identified. This pattern of pathologic features supports the idea that primary defects in neuronal migration, neurogenesis and aging may underlie the neuropathology reported in FXS.
Figures

References
-
- Hagerman RJ, Rivera SM, Hagerman PJ. The fragile X family of disorders: A model for autism and targeted treatments. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2008;4:40–52. doi: 10.2174/157339608783565770. - DOI
-
- Rogers SJ, Wehner EA, Hagerman RJ. The behavioral phenotype in fragile X: Symptoms of autism in very young children with fragile X syndrome, idiopathic autism, and other developmental disorders. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2001;22:409–417. - PubMed
-
- Hatton DD, Sideris J, Skinner M, Mankowski J, Bailey DB Jr, Roberts JE, Mirrett P. Autistic behavior in children with fragile X syndrome: Prevalence, stability, and the impact of FMRP. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140:1804–1813. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

