FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System with TRUstart algorithm, a 1-hour warm-up time
- PMID: 21303631
- PMCID: PMC3045239
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681100500114
FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System with TRUstart algorithm, a 1-hour warm-up time
Abstract
Background: The first-generation FreeStyle Navigator® Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (FreeStyle Navigator CGM) requires a 10 h warm-up period to avoid inaccurate glucose readings caused by sensor insertion trauma and wound-healing processes. The performance of a second-generation FreeStyle Navigator CGM that begins reporting glucose 1 h after sensor insertion is described.
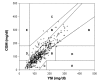
Methods: Second-generation FreeStyle Navigator CGM performance was evaluated in an in-clinic study using the YSI Model 2300 STATPlus Glucose Analyzer as reference with 47 subjects with type 1 diabetes. The reference readings were taken at 15 min intervals, and the study was designed to emphasize the first 10 h of use.
Results: The second-generation FreeStyle Navigator CGM exhibited continuous glucose error grid analysis ratings of 93.7% "clinically accurate," 3.6% "benign errors," and 2.8% "clinical errors" and a mean and median absolute relative difference of 14.5% and 10.7%, respectively. The second-generation algorithm detected signal instability in the first 10 h of use and suspended the reporting of 14.1% of first day continuous glucose readings. The clinical accuracy of the second-generation FreeStyle Navigator CGM was similar for the first 10 h versus subsequent hours, with 92.6% and 94.2% "clinically accurate" readings, respectively.
Conclusion: The warm-up period for the second-generation FreeStyle Navigator CGM was reduced from 10 to 1 h, with minimal interruption of glucose reporting and without sacrificing clinical performance.
© 2010 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
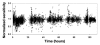



References
-
- Weinstein RL, Schwartz SL, Bragz RL, Bugler JR, Peyser TA, McGarraugh GV. Accuracy of the 5-day FreeStyle Navigator continuous glucose monitoring system: comparison with frequent laboratory reference measurements. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(5):1125–1130. - PubMed
-
- Rebrin K, Steil GM, van Antwerp WP, Mastrototaro JJ. Subcutaneous glucose predicts plasma glucose independent of insulimplications for continuous monitoring. Am J Physiol. 1999;277(3 Pt 1):E561–E571. - PubMed
-
- Kovatchev BP, Gonder-Frederick LA, Cox DJ, Clarke WL. Evaluating the accuracy of continuous glucose-monitoring sensors: continuous glucose-error grid analysis illustrated by TheraSense Freestyle Navigator data. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(8):1922–1928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

