Differential role of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein in Toll-like receptor 2-mediated regulation of gene expression of hepatic cytokines and drug-metabolizing enzymes
- PMID: 21303924
- PMCID: PMC3082375
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.110.037382
Differential role of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein in Toll-like receptor 2-mediated regulation of gene expression of hepatic cytokines and drug-metabolizing enzymes
Abstract
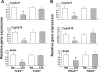
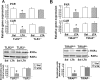
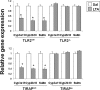
Pharmacological activities of drugs are impaired during inflammation because of reduced expression of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme genes (DMEs) and their regulatory nuclear receptors (NRs): pregnane X receptor (PXR), constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), and retinoid X receptor (RXRα). We have shown that a component of Gram-positive bacteria, lipoteichoic acid (LTA) induces proinflammatory cytokines and reduces gene expression of hepatic DMEs and NRs. LTA is a Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) ligand, which initiates signaling by recruitment of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP) to the cytoplasmic TIR domain of TLR2. To determine the role of TIRAP in TLR2-mediated regulation of DME genes, TLR2(+/+), TLR2(-/-), TIRAP(+/+), and TIRAP(-/-) mice were given LTA injections. RNA levels of the DMEs (Cyp3a11, Cyp2b10, and sulfoaminotransferase), xenobiotic NRs (PXR and CAR), and nuclear protein levels of the central NR RXRα were reduced ∼ 50 to 60% in LTA-treated TLR2(+/+) but not in TLR2(-/-) mice. Induction of hepatic cytokines (interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-6), c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor-κΒ was blocked in TLR2(-/-) mice. As expected, expression of hepatic DMEs and NRs was reduced by LTA in TIRAP(+/+) but not in TIRAP(-/-) mice. Of interest, cytokine RNA levels were induced in the livers of both the TIRAP(+/+) and TIRAP(-/-) mice, whereas LTA-mediated induction of serum cytokines was attenuated in TIRAP(-/-) mice. LTA-mediated down-regulation of DME genes was attenuated in hepatocytes from TLR2(-/-) or TIRAP(-/-) mice and in small interfering RNA-treated hepatocytes. Thus, the effect of TLR2 on DME genes in hepatocytes was mediated by TIRAP, whereas TIRAP was not involved in mediating the effects of TLR2 on cytokine expression in the liver.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme genes by Toll-like receptor 4 signaling is independent of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein.Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Jan;36(1):95-101. doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.018051. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008. PMID: 17932222
-
Role of constitutive androstane receptor in Toll-like receptor-mediated regulation of gene expression of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters.Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Jan;42(1):172-81. doi: 10.1124/dmd.113.053850. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014. PMID: 24194512 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters by the Toll-like receptor 2 ligand, lipoteichoic acid.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009 Jan 1;481(1):123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.10.003. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009. PMID: 18940178 Free PMC article.
-
[TIR domain--containing adaptors regulate TLR-mediated signaling pathways].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Dec;62(12):2197-203. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15597785 Review. Japanese.
-
Nuclear receptor-mediated transcriptional regulation in Phase I, II, and III xenobiotic metabolizing systems.Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2006 Dec;21(6):437-57. doi: 10.2133/dmpk.21.437. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2006. PMID: 17220560 Review.
Cited by
-
E. coli infection modulates the pharmacokinetics of oral enrofloxacin by targeting P-glycoprotein in small intestine and CYP450 3A in liver and kidney of broilers.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):e87781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087781. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498193 Free PMC article.
-
Drug disposition in pathophysiological conditions.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Nov;13(9):1327-44. doi: 10.2174/138920012803341302. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22746301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in drug-drug interaction between paclitaxel and irinotecan in vitro.Toxicol In Vitro. 2017 Jun;41:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.02.019. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017. PMID: 28242239 Free PMC article.
-
CYP3A-dependent drug metabolism is reduced in bacterial inflammation in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;166(7):2176-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01933.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22394353 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling of genes and pathways associated with arsenic toxicity and tolerance in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Apr 16;14:94. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-94. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24734953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511 - PubMed
-
- Ashino T, Oguro T, Shioda S, Horai R, Asano M, Sekikawa K, Iwakura Y, Numazawa S, Yoshida T. (2004) Involvement of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α in CYP3A11 and 2C29 down-regulation by bacillus Calmette-Guerin and lipopolysaccharide in mouse liver. Drug Metab Dispos 32:707–714 - PubMed
-
- Assenat E, Gerbal-Chaloin S, Larrey D, Saric J, Fabre JM, Maurel P, Vilarem MJ, Pascussi JM. (2004) Interleukin 1β inhibits CAR-induced expression of hepatic genes involved in drug and bilirubin clearance. Hepatology 40:951–960 - PubMed
-
- Cheng PY, Wang M, Morgan ET. (2003) Rapid transcriptional suppression of rat cytochrome P450 genes by endotoxin treatment and its inhibition by curcumin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:1205–1212 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

