PIPKIγ regulates β-catenin transcriptional activity downstream of growth factor receptor signaling
- PMID: 21303971
- PMCID: PMC3066690
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2480
PIPKIγ regulates β-catenin transcriptional activity downstream of growth factor receptor signaling
Abstract
Increased β-catenin transcriptional activity downstream of the Wnt/Wingless signaling pathway has been observed in many human tumors, most notably colorectal carcinomas. However, β-catenin activation is also observed in many human malignancies with no observable Wnt activity. Wnt-independent pathways that activate β-catenin remain undefined, yet have the potential to play a significant role during tumorigenesis. Here, we report that phosphotidylinositol phosphate kinase Iγ (PIPKIγ), an enzyme that generates phosphoinositide messengers in vivo, directly associates with β-catenin and increases β-catenin activity downstream of growth factor stimulation. PIPKIγ expression and kinase activity enhance β-catenin phosphorylation on residues that promote nuclear importation and transcriptional activity. Lastly, we show that β-catenin is required for PIPKIγ-dependent increased cell proliferation. These results reveal a novel mechanism in which PIPKIγ expression and catalytic activity enhance β-catenin nuclear translocation and expression of its target genes to promote tumorigenic phenotypes.
©2011 AACR.
Figures
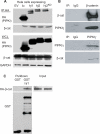
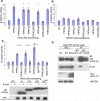


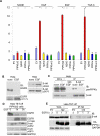

References
-
- Brembeck FH, Rosario M, Birchmeier W. Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of beta-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16(1):51–9. - PubMed
-
- Kemler R. From cadherins to catenins: cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion. Trends Genet. 1993;9(9):317–21. - PubMed
-
- Desbois-Mouthon C, Cadoret A, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ, et al. Insulin and IGF-1 stimulate the beta-catenin pathway through two signalling cascades involving GSK-3beta inhibition and Ras activation. Oncogene. 2001;20(2):252–9. - PubMed
-
- Lu Z, Ghosh S, Wang Z, Hunter T. Downregulation of caveolin-1 function by EGF leads to the loss of E-cadherin, increased transcriptional activity of beta-catenin, and enhanced tumor cell invasion. Cancer Cell. 2003;4(6):499–515. - PubMed
-
- Moon RT, Bowerman B, Boutros M, Perrimon N. The promise and perils of Wnt signaling through beta-catenin. Science. 2002;296(5573):1644–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

