Chromatin remodelling complex dosage modulates transcription factor function in heart development
- PMID: 21304516
- PMCID: PMC3096875
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1187
Chromatin remodelling complex dosage modulates transcription factor function in heart development
Abstract
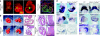
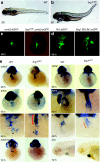
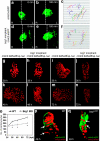
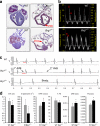
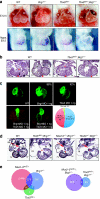
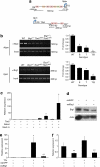
Dominant mutations in cardiac transcription factor genes cause human inherited congenital heart defects (CHDs); however, their molecular basis is not understood. Interactions between transcription factors and the Brg1/Brm-associated factor (BAF) chromatin remodelling complex suggest potential mechanisms; however, the role of BAF complexes in cardiogenesis is not known. In this study, we show that dosage of Brg1 is critical for mouse and zebrafish cardiogenesis. Disrupting the balance between Brg1 and disease-causing cardiac transcription factors, including Tbx5, Tbx20 and Nkx2-5, causes severe cardiac anomalies, revealing an essential allelic balance between Brg1 and these cardiac transcription factor genes. This suggests that the relative levels of transcription factors and BAF complexes are important for heart development, which is supported by reduced occupancy of Brg1 at cardiac gene promoters in Tbx5 haploinsufficient hearts. Our results reveal complex dosage-sensitive interdependence between transcription factors and BAF complexes, providing a potential mechanism underlying transcription factor haploinsufficiency, with implications for multigenic inheritance of CHDs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Baf60c is essential for function of BAF chromatin remodelling complexes in heart development.Nature. 2004 Nov 4;432(7013):107-12. doi: 10.1038/nature03071. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15525990
-
Dynamic BAF chromatin remodeling complex subunit inclusion promotes temporally distinct gene expression programs in cardiogenesis.Development. 2019 Jul 5;146(19):dev174086. doi: 10.1242/dev.174086. Development. 2019. PMID: 30814119 Free PMC article.
-
Functional redundancy of SWI/SNF catalytic subunits in maintaining vascular endothelial cells in the adult heart.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 17;111(5):e111-22. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.265587. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22740088 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in cardiac development and disease.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2012 Jan;44(1):92-102. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmr090. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2012. PMID: 22194017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of chromatin remodeling BAF complex in neural differentiation and reprogramming.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Jun;356(3):575-84. doi: 10.1007/s00441-013-1791-7. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 24496512 Review.
Cited by
-
ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complex in the Lineage Specification of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Sep 9;2020:8839703. doi: 10.1155/2020/8839703. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32963551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct tissue-specific requirements for the zebrafish tbx5 genes during heart, retina and pectoral fin development.Open Biol. 2014 Apr 23;4(4):140014. doi: 10.1098/rsob.140014. Open Biol. 2014. PMID: 24759614 Free PMC article.
-
Sall1 transiently marks undifferentiated heart precursors and regulates their fate.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Mar;92:158-62. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Feb 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26876450 Free PMC article.
-
T-box family of transcription factor-TBX5, insights in development and disease.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Feb 15;9(2):442-453. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28337273 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Mammalian Cardiomyocyte Development.Epigenomes. 2024 Jun 29;8(3):25. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8030025. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 39051183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srivastava D. Making or breaking the heart: from lineage determination to morphogenesis. Cell 126, 1037–1048 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Bruneau B. G. The developmental genetics of congenital heart disease. Nature 451, 943–948 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Bruneau B. G. et al.. A murine model of Holt-Oram syndrome defines roles of the T-box transcription factor Tbx5 in cardiogenesis and disease. Cell 106, 709–721 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Garg V. et al.. GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature 424, 443–447 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

