Epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number aberration at the primary tumour is significantly associated with extracapsular spread in oral cancer
- PMID: 21304522
- PMCID: PMC3048213
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.22
Epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number aberration at the primary tumour is significantly associated with extracapsular spread in oral cancer
Abstract
Background: Extracapsular spread (ECS) of lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancers, including oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCCs), is known to reflect tumour aggressiveness, and is significantly associated with high rates of loco-regional recurrence, distant metastasis, and poor outcome. The purpose of this study was to confirm ECS as an important prognostic indicator and to determine the significant factors associated with ECS in OSCCs.
Methods: We investigated the incidence of ECS and impact of ECS on survival in 127 OSCC patients. To determine the factors significantly correlated with ECS, we examined many factors, including the clinicopathological features of primary tumours, lymph node metastasis, and copy number aberrations of the cyclin D1 gene (CCND1) and epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR) at primary tumours, and evaluated the value of predicting the risk of ECS of the metastatic lymph node.
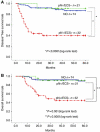
Results: Kaplan-Meier and multivariate disease-free and overall survival analysis clearly demonstrated that ECS is an independent prognostic factor in OSCCs. Moreover, logistic regression analysis showed that the number of pathologically positive nodes and copy number aberrations of EGFR at the primary tumour are independent predictors of ECS.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that ECS is an independent prognostic factor in OSCCs. Moreover, the number of pathologically positive lymph nodes and EGFR numerical aberrations of the primary tumour were also shown to be excellent predictors of ECS in OSCCs. Preoperative evaluation of EGFR numerical aberrations might therefore be a useful tool for selecting patients at high risk of ECS, who would benefit from targeted aggressive multimodality therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Alvi A, Johnson JT (1996) Extracapsular spread in the clinically negative neck (N0): implications and outcome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 114: 65–70 - PubMed
-
- Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, Fu KK, Milas L (2002) Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 62: 7350–7356 - PubMed
-
- Arany I, Chen SH, Megyesi JK, Adler-Storthz K, Chen Z, Rajaraman S, Ember IA, Tyring SK, Brysk MM (2003) Differentiation-dependent expression of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) might modify responses to growth factors in the cancers of the head and neck. Cancer Lett 199: 83–89 - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL (2002) Epidermal growth factor receptor dependence in human tumors: more than just expression? Oncologist 7(Suppl 4): 31–39 - PubMed
-
- Bei R, Budillon A, Masuelli L, Cereda V, Vitolo D, Di Gennaro E, Ripavecchia V, Palumbo C, Ionna F, Losito S, Modesti A, Kraus MH, Muraro R (2004) Frequent overexpression of multiple ErbB receptors by head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contrasts with rare antibody immunity in patients. J Pathol 204: 317–325 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous