Induction of the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 is involved in stress-induced hippocampal damage
- PMID: 21304589
- PMCID: PMC3029367
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016447
Induction of the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 is involved in stress-induced hippocampal damage
Abstract
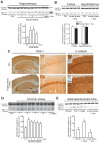
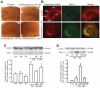
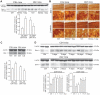
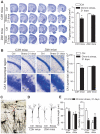
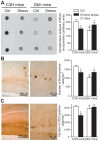
The identification of mechanisms that mediate stress-induced hippocampal damage may shed new light into the pathophysiology of depressive disorders and provide new targets for therapeutic intervention. We focused on the secreted glycoprotein Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1), an inhibitor of the canonical Wnt pathway, involved in neurodegeneration. Mice exposed to mild restraint stress showed increased hippocampal levels of Dkk-1 and reduced expression of β-catenin, an intracellular protein positively regulated by the canonical Wnt signalling pathway. In adrenalectomized mice, Dkk-1 was induced by corticosterone injection, but not by exposure to stress. Corticosterone also induced Dkk-1 in mouse organotypic hippocampal cultures and primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and, at least in the latter model, the action of corticosterone was reversed by the type-2 glucocorticoid receptor antagonist mifepristone. To examine whether induction of Dkk-1 was causally related to stress-induced hippocampal damage, we used doubleridge mice, which are characterized by a defective induction of Dkk-1. As compared to control mice, doubleridge mice showed a paradoxical increase in basal hippocampal Dkk-1 levels, but no Dkk-1 induction in response to stress. In contrast, stress reduced Dkk-1 levels in doubleridge mice. In control mice, chronic stress induced a reduction in hippocampal volume associated with neuronal loss and dendritic atrophy in the CA1 region, and a reduced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Doubleridge mice were resistant to the detrimental effect of chronic stress and, instead, responded to stress with increases in dendritic arborisation and neurogenesis. Thus, the outcome of chronic stress was tightly related to changes in Dkk-1 expression in the hippocampus. These data indicate that induction of Dkk-1 is causally related to stress-induced hippocampal damage and provide the first evidence that Dkk-1 expression is regulated by corticosteroids in the central nervous system. Drugs that rescue the canonical Wnt pathway may attenuate hippocampal damage in major depression and other stress-related disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brouwer JP, Appelhof BC, Hoogendijk WJ, Huyser J, Endert E, et al. Thyroid and adrenal axis in major depression: a controlled study in outpatients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005;152:185–191. - PubMed
-
- Brown ES, Varghese FP, McEwen BS. Association of depression with medical illness: does cortisol play a role? Biol Psychiatry. 2004;55:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Parker KJ, Schatzberg AF, Lyons DM. Neuroendocrine aspects of hypercortisolism in major depression. Horm Behav. 2003;43:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Sapolsky RM. Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:925–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

