Evaluation of the antioxidant, antibacterial, and antiproliferative activities of the acetone extract of the roots of Senna italica (Fabaceae)
- PMID: 21304625
- PMCID: PMC3021157
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v7i2.50873
Evaluation of the antioxidant, antibacterial, and antiproliferative activities of the acetone extract of the roots of Senna italica (Fabaceae)
Abstract
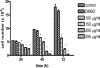
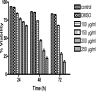
Senna italica, a member of the Fabaceae family (subfamily Caesalpinaceae), is widely used traditionally to treat a number of disease conditions, such as sexually transmitted diseases and some forms of intestinal complications. The roots of Senna italica were collected from Zebediela subregion, Limpopo province (S.A), powdered and extracted with acetone by cold/shaking extraction method. The phytochemical composition of the extract was determined by thin layer chromatography (TLC). The chromatograms were visualised with vanillin-sulphuric acid and p-anisaldehyde reagents. The total phenolic content of the extract was determined by Folin-Ciocalteu method and expressed as TAE/g dry weight. The extract was assayed for the in vitro anticancer activity using Jurkat T cells, antioxidant activity using DPPH assay and antibacterial activity by bioautographic method and the microtitre plate method. The acetone extract of the roots of Senna italica inhibited the growth of Jurkat T cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The extract also had free radical scavenging activity as well as reasonable antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus with MICs ranging from 0,08 to 0.16 mg/ml in the same order as ampicillin the positive control. The biological activities observed in the acetone extract validated the ethnomedicinal use of Senna italica.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Antioxidant; Antiproliferative; Senna italica.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Rationale for using Peltophorum africanum (Fabaceae) extracts in veterinary medicine.J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2005 Jun;76(2):54-8. doi: 10.4102/jsava.v76i2.397. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2005. PMID: 16108521
-
Polarity of extracts and fractions of four Combretum (Combretaceae) species used to treat infections and gastrointestinal disorders in southern African traditional medicine has a major effect on different relevant in vitro activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Jun 11;154(2):339-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.030. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24681040
-
Phytochemical screening and evaluation of in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the indigenous medicinal plant Albizia odoratissima.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):1155-1161. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1291694. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 28219296 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Recent Studies on the Antioxidant and Anti-Infectious Properties of Senna Plants.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 4;2022:6025900. doi: 10.1155/2022/6025900. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35154569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cassia spectabilis (DC) Irwin et Barn: a promising traditional herb in health improvement.Molecules. 2012 Aug 29;17(9):10292-305. doi: 10.3390/molecules170910292. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22932211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tswana traditional health practitioners' perspectives on the management of diabetes and hypertension: a qualitative study using focus group discussions.Pan Afr Med J. 2019 Oct 16;34:93. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2019.34.93.19112. eCollection 2019. Pan Afr Med J. 2019. PMID: 31934236 Free PMC article.
-
Pentachlorophenol induction of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa mexAB-oprM efflux operon: involvement of repressors NalC and MexR and the antirepressor ArmR.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032684. Epub 2012 Feb 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22393435 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial interactions, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic effects of four medicinal plant species.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jul 3;18(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2264-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29970064 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Extracts of Viscum continuum E. Mey. Ex Sprague, a South African Mistletoe.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 12;11(16):2094. doi: 10.3390/plants11162094. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015398 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant Activity, and Acute Toxicity Evaluation of Senna italica Extract Used in Traditional Medicine.J Toxicol. 2023 Mar 17;2023:6405415. doi: 10.1155/2023/6405415. eCollection 2023. J Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36968147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdille MH, Singh RP, Jayaprakasha GK, Jena BS. Antioxidant activity of the extracts from Dillenia fruits. J Food Chem. 2005;90:891–896.
-
- Ali, Bu-Bashir AK, Tamira MO. Some effects of C. italica on the central nervous system in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1997;49(5):500–504. - PubMed
-
- Altaman SA, Randers L, Rao G. Comparison of trypton blue dye exclusion and fluorometric assays for mammalian determinations. Biotechnol Prog. 2008;9(6):671–674. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa FG, da Conceicao M, de Oliveira F, Braz-Filho R, Silveira ER. Anthraquinones and naphthopyrones from Senna rugosa. Biochem Sys Ecol. 2004;32:363–365.
-
- Begue WJ, Kline RM. The use of tetrazolium salts in bioautographic procedure. J Chromatogr. 1972;88:182–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
