Complete genome sequence of Desulfomicrobium baculatum type strain (X)
- PMID: 21304634
- PMCID: PMC3035215
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.13134
Complete genome sequence of Desulfomicrobium baculatum type strain (X)
Abstract
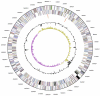
Desulfomicrobium baculatum is the type species of the genus Desulfomicrobium, which is the type genus of the family Desulfomicrobiaceae. It is of phylogenetic interest because of the isolated location of the family Desulfomicrobiaceae within the order Desulfovibrionales. D. baculatum strain X(T) is a Gram-negative, motile, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from water-saturated manganese carbonate ore. It is strictly anaerobic and does not require NaCl for growth, although NaCl concentrations up to 6% (w/v) are tolerated. The metabolism is respiratory or fermentative. In the presence of sulfate, pyruvate and lactate are incompletely oxidized to acetate and CO(2). Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. This is the first completed genome sequence of a member of the deltaproteobacterial family Desulfomicrobiaceae, and this 3,942,657 bp long single replicon genome with its 3494 protein-coding and 72 RNA genes is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: Desulfomicrobiaceae; Gram-negative; Sulfate reducer; anaerobe; free-living; freshwater; mesophile; non-pathogenic.
Figures


References
-
- Rozanova EP, Nazina TN. A mesophilic, sulfate-reducing, rod-shaped, nonsporeforming bacterium. Mikrobiologiya 1976; 45:825-830 - PubMed
-
- List Editor Validation of the publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the ISJB. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1984; 34:355-357
-
- Rozanova EP, Nazina TN, Galushko AS. Isolation of a new genus of sulfate-reducing bacteria and description of a new species of this genus, Desulfomicrobium apsheronum gen. nov., sp. nov. Mikrobiologiya 1988; 57:634-641
-
- Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17:540-552 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

